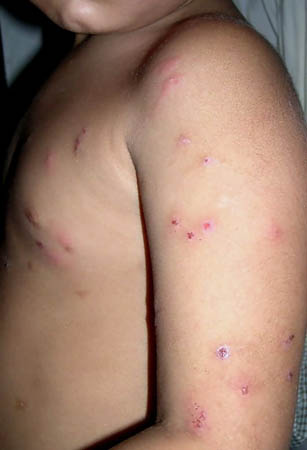
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- acute to subacute recurrent skin eruption
- polymorphic, generalized, nonpruritic skin eruption
Other diagnostic factors
- scars or pigment changes
- immunosuppression
- recent illness
- family history of pityriasis lichenoides
- headache
- myalgias/arthralgias
- malaise
- burning/pruritus
- multiorgan failure
Risk factors
- childhood to early adult age
- male sex
- HIV
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- dermoscopy
- skin biopsy
Tests to consider
- antistreptolysin titers
- Epstein-Barr virus IgM/IgG viral capsid antigen and nuclear antigen antibody
- monospot or heterophil antibody test
- hepatitis B surface antigen, antisurface antibody, and anticore IgM
- hepatitis C virus antibody
- HIV screening
- rapid plasma reagin
- throat cultures
- toxoplasma Sabin-Feldman dye test, indirect immunofluorescence/hemagglutination
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CRP
- serum LDH
- WBC count
- serum albumin
Treatment algorithm
mild to moderate disease
severe disease or treatment resistance
Contributors
Authors
Amy Musiek, MD
Professor of Dermatology
Division of Dermatology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
St. Louis
MO
Divulgaciones
AM is a paid lecturer in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma for Dermatology Week, is the author of the UpToDate article on Pityriasis lichenoides chronica, and is an investigator for multiple industry sponsored studies all unrelated to pityriasis lichenoides.
Agradecimientos
Dr Amy Musiek would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Amer Khachemoune and Dr Marianna Blyumin-Karasik, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
AK and MB-K declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Andrew D. Lee, MD
Resident
Department of Dermatology
Wake Forest University School of Medicine
Winston-Salem
NC
Divulgaciones
ADL declares that he has no competing interests.
Abdulhafez Selim, MD
Assistant Professor
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
Dhahran
Saudi Arabia
Divulgaciones
AS declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Khachemoune A, Blyumin ML. Pityriasis lichenoides: pathophysiology, classification, and treatment review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8(1):29-36. Resumen
Bowers S, Warshaw EM. Pityriasis lichenoides and its subtypes. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 Oct;55(4):557-72; quiz 573-6. Resumen
Bellinato F, Maurelli M, Gisondi P, et al. A systematic review of treatments for pityriasis lichenoides. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Nov;33(11):2039-49. Resumen
Jung F, Sibbald C, Bohdanowicz M, et al. Systematic review of the efficacies and adverse effects of treatments for pityriasis lichenoides. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Dec;183(6):1026-32. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
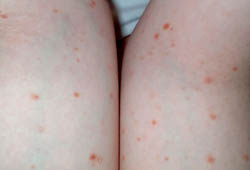
Diferenciales
- Lymphomatoid papulosis
- Guttate psoriasis
- Drug eruption
Más DiferencialesFolletos para el paciente
Psoriasis: what is it?
Psoriasis: what are the treatment options?
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad