Summary
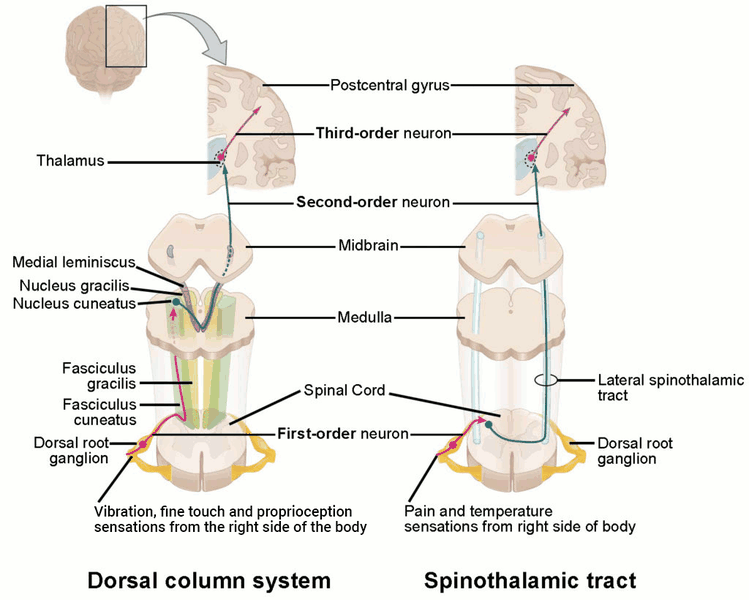
Differentials
Common
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Ulnar neuropathy at elbow (UNE)
- Fibular (peroneal) neuropathy
- Meralgia paresthetica
- Cervical radiculopathy
- Thoracic radiculopathy
- Lumbosacral radiculopathy
- Spinal cord compression
- Multiple sclerosis
- Distal symmetric polyneuropathy (DSP)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Vitamin B1 deficiency
- Vitamin B6 deficiency or excess
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Vitamin E deficiency
- Drug toxicity
- Alcoholic neuropathy
- Stroke/transient ischemic attack
- Migraine with aura
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Panic attack with hyperventilation
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease
- Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN)
- Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy (HNPP)
Uncommon
- Brachial plexopathy
- Lumbosacral plexopathy
- Tibial neuropathy
- Trigeminal neuropathy
- Acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP)
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating sensory polyradiculopathy (CISP)
- Uremia
- Hypocalcemia
- Copper deficiency
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Radiation
- Hexane exposure
- Ciguatera or saxitoxin poisoning
- HIV neuropathy
- Leprosy
- Herpes simplex infection
- Neurosyphilis
- Herpes zoster infection (shingles)
- Lyme disease
- Functional neurologic and somatic symptom disorders
- Inborn errors of metabolism
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Churg-Strauss syndrome
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener granulomatosis)
- Polyarteritis nodosa
- Microscopic polyangiitis
- Sjogren syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Monoclonal protein production
- Focal seizures
- Paraneoplastic sensory neuropathy or ganglionopathy
- Intravascular lymphoma
- Neuro-Behcet disease
- Wartenberg migrant sensory neuritis
- Numb chin syndrome
- Peripheral neuropathy after bariatric surgery
- Notalgia paresthetica
- Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (Devic disease)
- Anti-myelin-associated glycoproteins (MAG) peripheral neuropathy
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV)
Contributors
Authors
Nigel Ashworth, MBChB, MSc, FRCP(Can)
Professor
Division of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry
University of Alberta
Edmonton
Canada
Disclosures
NA declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Nigel Ashworth would like to gratefully acknowledge the late Dr Caroline M. Klein for her contribution to this topic.
Disclosures
CMK authored a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Richard W. Orrell, BSc, MD, FRCP
Senior Lecturer and Consultant Neurologist
Department of Clinical Neuroscience
UCL Institute of Neurology
London
UK
Disclosures
RWO declares that he has no competing interests.
Brian Christopher Callaghan, MD, MS
Professor of Neurology
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
Research contracts from AAN and editorial support. Dynamed consultant.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
England JD, Gronseth GS, Franklin G, et al. Practice parameter: evaluation of distal symmetric polyneuropathy: role of laboratory and genetic testing (an evidence-based review). Report of the American Academy of Neurology, American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology. 2009 Jan 13;72(2):185-92.Full text Abstract
Jacoby N, Anziska Y. A practical approach to diagnosing peripheral neuropathies. Semin Neurol. 2025 Feb;45(1):4-12.Full text Abstract
England JD, Franklin G, Gjorvad G, et al. Quality improvement in neurology: distal symmetric polyneuropathy quality measures. Neurology. 2014 May 13;82(19):1745-8.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Patient information
Anxiety
Diabetes type 1: what is it?
More Patient informationVideos
Diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults: animated demonstration
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer