Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- visual field loss
Other diagnostic factors
- headache
- transient visual obscurations
- pulse-synchronous tinnitus
- photophobia
- retrobulbar pain
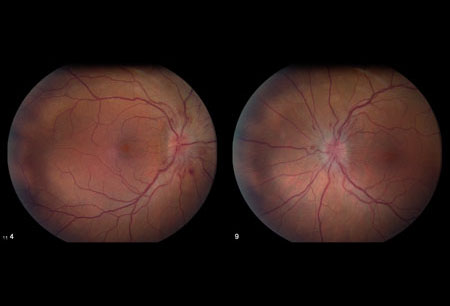
- optical disk swelling
- decreased visual acuity
- ocular motility disturbances
- relative afferent pupillary defect
Risk factors
- female sex
- obesity and weight gain
- certain medication use
- associated causal diseases
- sleep apnea
- family history
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- visual field testing (perimetry)
- dilated fundoscopy
- visual acuity
- MRI of brain with or without contrast
- lumbar puncture at spinal L3/L4
Tests to consider
- magnetic resonance venogram of head
- optical coherence tomography
Treatment algorithm
all patients
Contributors
Authors
Michael Wall, MD
Professor
Department of Neurology and Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences
University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics and Iowa City VA Health Care System
Iowa City
IA
Divulgaciones
MW is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Mansoor Mughal, MD
Retina Fellow
Rutgers University
Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital
New Brunswick
NJ
Divulgaciones
MM declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Paul W. Brazis, MD
Consultant in Neurology and Neuro-Ophthalmology
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Divulgaciones
PWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Tim D. Matthews, MBBS
Consultant Neuro-ophthalmologist
Birmingham Neuro-ophthalmology Unit
University Hospital Birmingham
Birmingham
UK
Divulgaciones
TDM declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Wall M. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurol Clin. 2010 Aug;28(3):593-617.Texto completo Resumen
Johnson LN, Krohel GB, Madsen RW, et al. The role of weight loss and acetazolamide in the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Ophthalmology. 1998 Dec;105(12):2313-7. Resumen
Hayreh SS. Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc (papilloedema): a preliminary report. Br J Ophthalmol. 1964 Oct;48:522-43.Texto completo Resumen
Smith JL. Whence pseudotumor cerebri? J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1985 Mar;5(1):55-6. Resumen
Frisen L. Swelling of the optic nerve head: a staging scheme. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Jan;45(1):13-8.Texto completo Resumen
NORDIC Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Study Group Writing Committee; Wall M, McDermott MP, Kieburtz KD, et al. Effect of acetazolamide on visual function in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension and mild visual loss: the idiopathic intracranial hypertension treatment trial. JAMA. 2014 Apr 23-30;311(16):1641-51.Texto completo Resumen
Hoffmann J, Mollan SP, Paemeleire K, et al. European Headache Federation guideline on idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Headache Pain. 2018 Oct 8;19(1):93.Texto completo Resumen
Sinclair AJ, Burdon MA, Nightingale PG, et al. Low energy diet and intracranial pressure in women with idiopathic intracranial hypertension: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2010 Jul 7;341:c2701.Texto completo Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Intracranial structural anomalies
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- European Headache Federation guideline on idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Obesity - drugs and surgery
Tinnitus
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad