Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- newborn and toddler age
- abnormal location of urethra
- incomplete prepuce
- penile curvature and/or torsion
- recent genital exam or procedure
- history of short or small penis
- penile pain and swelling
- foreskin adherent to glans
- penile adhesions and smegma
- penile cicatrix
- penile glans edema
- prominent prepubic fat pad
- presence of hernia or hydrocele
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- forced retraction of foreskin
- dyspareunia
- recent penile trauma
- history of balanitis or balanoposthitis
- urinary obstruction or retention
- necrosis of penile skin
- discoloration of glans
- penile length discrepancy
- history of urinary tract infection
- history of pelvic or genitourinary surgery
- erectile dysfunction
Fatores de risco
- uncircumcised penis (paraphimosis)
- indwelling urinary catheter (paraphimosis)
- parental unawareness (phimosis)
- balanitis xerotica obliterans (phimosis)
- penile trauma (phimosis)
- recurrent balanitis and balanoposthitis (phimosis)
- low birth weight (hypospadias)
- preterm delivery (hypospadias)
- gestational diabetes, maternal obesity, maternal hypertension, older maternal age (hypospadias)
- family history (hypospadias, congenital penile curvature and/or torsion)
- obesity (buried penis)
- circumcision (trapped penis)
- penile and lower abdominal scarring (buried penis)
- hernia or hydrocele (buried penis)
- SRD5A2 gene V89L polymorphism (hypospadias)
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- clinical diagnosis
Algoritmo de tratamento
prepubertal phimosis, congenital or physiologic
postpubertal phimosis
paraphimosis
hypospadias
congenital penile curvature and/or torsion
concealed penis <3 years old (before toilet training)
concealed penis ≥3 years old (after toilet training)
micropenis
Colaboradores
Autores
Kathleen Kieran, MD, MSc, MME
Director of Pediatric Urology Fellowship
Professor and Vice Chair for Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
Department of Urology
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
Declarações
KK declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Kathleen Kieran would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Nicol Corbin Bush, Dr Nicholas Cost, Dr Linda Baker, and Dr Michael Holzer, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
NCB, NC, LB, and MH declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
David Bloom, MD
Chair
Department of Urology
The Jack Lapides Professor of Urology
University of Michigan Medical School
Ann Arbor
MI
Declarações
DB declares that he has no competing interests.
Vincent Gnanapragasam, MBBS, BMedSci, PhD, FRCSEng, FRCSEd(Urol)
Lecturer in Uro-oncology and Consultant Urological Surgeon
Department of Urology
Addenbrooke's Hospital
Cambridge
UK
Declarações
VG declares that he has no competing interests.
Laurence Baskin, MD
Chief
Pediatric Urology
and Professor
Urology and Pediatrics
UCSF Children's Hospital
San Francisco
CA
Declarações
LB declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].Texto completo
Dave S, Afshar K, Braga LH, et al. Canadian Urological Association guideline on the care of the normal foreskin and neonatal circumcision in Canadian infants (full version). Can Urol Assoc J. 2018 Feb; 12(2):E76-99.Texto completo Resumo
British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Management of foreskin conditions. Jun 2006 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
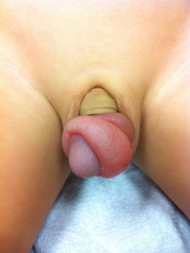
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Balanoposthitis
- Encircling foreign body
- Trapped penis
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisგაიდლაინები
- EAU guidelines on paediatric urology
- Penile circumcision
Mais გაიდლაინებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას