Summary
Definition
History and exam
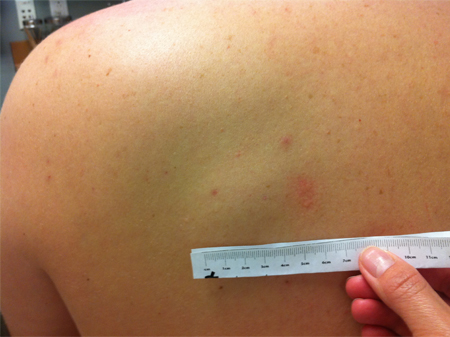
Key diagnostic factors
- cutaneous mass <5 cm diameter
- soft cutaneous mass
- mobile cutaneous mass
- superficial cutaneous mass
Other diagnostic factors
- painless cutaneous mass
- gastrointestinal obstruction
- gastrointestinal bleeding
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition
- trauma
- heavy alcohol consumption
Diagnostic tests
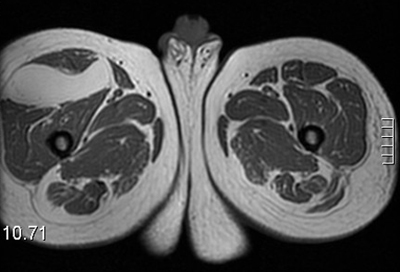
Tests to consider
- ultrasound
- MRI
- CT scan
- core needle biopsy
- incisional biopsy
- excisional biopsy
- upper gastrointestinal contrast study
- gastrointestinal endoscopy
Treatment algorithm
superficial cutaneous lipoma on trunk or extremity
Dercum disease
symptomatic gastrointestinal lipoma
lipoma in atypical site
Contributors
Authors
Kimberly Moore Dalal, MD
Medical Director, Surgical Oncology
General Surgery
Mills-Peninsula Hospital
Palo Alto Medical Foundation
Burlingame
CA
Disclosures
KMD is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Steven D. DeMartini, MD
Staff Pathologist
Oroville Hospital
Oroville
CA
Disclosures
SDD declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
William Tseng, MD
Associate Professor of Surgery
City of Hope National Medical Center
Duarte
CA
Disclosures
WT declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Primary Care Dermatology Society. Lipoma. Nov 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Noebauer-Huhmann IM, Weber MA, Lalam RK, et al. Soft tissue tumors in adults: ESSR-approved guidelines for diagnostic imaging. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2015 Dec;19(5):475-82. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Liposarcoma
- Epidermoid cyst
- Abscess
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Soft tissue masses
- Clinical guidance: lipoma
More GuidelinesVideos
Intradermal injection animation demonstration
Mais vídeosConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal