Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- upper abdominal/flank mass or swelling
- congenital urogenital anomalies
- congenital syndromes
Other diagnostic factors
- abdominal distension
- abdominal pain
- hypertension
- hematuria
- poor appetite, weight loss, and/or fever
- pallor
- shortness of breath
- hepatomegaly
- varicocele
- family history of Wilms tumor
- hypoglycemia in infancy
- features of paraneoplastic syndrome
Risk factors
- age <5 years
- congenital urogenital anomalies
- congenital syndromes
- family history of Wilms tumor
- prenatal exposure to harmful environmental factors
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- CBC
- renal function
- liver function tests
- urinalysis
- serum total protein/albumin
- coagulation studies
- serum calcium level
- abdominal ultrasound
- CT or MRI abdomen and pelvis
- CT chest (with or without contrast)
- chest x-ray
Investigations to consider
- tumor histology
- genetic testing
- tumor molecular biomarker testing
Treatment algorithm
COG criteria
SIOP criteria
tumor recurrence
Contributors
Authors
James Geller, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Peckham Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders
Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego
San Diego
CA
Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
Department of Pediatrics
University of California San Diego
La Jolla
CA
Disclosures
JG declares that he was "immediate past Chair" of the Children’s Oncology Group Renal Tumor Committee and is Chair of Children’s Oncology Group Protocol AREN1921. He has provided expert testimony and deposed in two Wilms tumor cases (without testifying). JG is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Nicholas G. Cost, MD
Associate Professor
Co-Director of the Surgical Oncology Program
Children’s Hospital Colorado
Program Director of the Pediatric Urology Fellowship
Chair of Renal Tumor Committee in Children’s Oncology Group (COG)
University of Colorado
Aurora
CO
Disclosures
NGC declares that his wife works as a Senior Medical Officer for Janssen Pharmaceuticals. NGC is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Daniel J. Benedetti, MD, MA
Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Hematology/Oncology
COG Renal Tumor Committee
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Nashville
TN
Divulgaciones
DJB declares that he has no competing interests. DJB is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Amy E. Armstrong, MD
Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
Division of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
COG Renal Tumor Committee
Washington University in St. Louis
St. Louis
MO
Divulgaciones
AEA declares that she has no competing interests. AEA is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Agradecimientos
Drs Geller, Cost, Benedetti, and Armstrong would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Sandeep Batra, the previous contributor to this topic.
Revisores por pares
Nadine Deannie Lee, MD
Pediatric Hematologist-Oncologist
Hematology/Oncology
Riley Children's Hospital
Indiana University Health
Indianapolis
IN
Divulgaciones
NDL declares that she has no competing interests.
Norbert Graf, MD
Direktor
Klinik für Pädiatrische Onkologie und Hämatologie
Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes
Homburg
Germany
Divulgaciones
NG declares that he has no competing interests.
Zelig Tochner, MD
Associate Professor
Radiation Oncology
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
ZT declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Spreafico F, Fernandez CV, Brok J, et al. Wilms tumour. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Oct 14;7(1):75.Full text Abstract
Geller JI, Hong AL, Vallance KL, et al. Children's Oncology Group's 2023 blueprint for research: renal tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2023 Sep;70 Suppl 6(suppl 6):e30586.Full text Abstract
Lopyan NM, Ehrlich PF. Surgical management of Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma) and renal cell carcinoma in children and young adults. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2021 Apr;30(2):305-23. Abstract
Vujanić GM, Parsons LN, D'Hooghe E, et al. Pathology of Wilms' tumour in International Society of Paediatric Oncology (SIOP) and Children's Oncology Group (COG) renal tumour studies: similarities and differences. Histopathology. 2022 Jun;80(7):1026-37. Abstract
van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Hol JA, Pritchard-Jones K, et al. Position paper: rationale for the treatment of Wilms tumour in the UMBRELLA SIOP-RTSG 2016 protocol. Nat Rev Urol. 2017 Dec;14(12):743-52.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
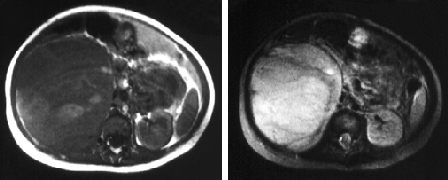
Differentials
- Neuroblastoma
- Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney
- Renal cell carcinoma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma)
- Long-term follow-up guidelines for survivors of childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancers
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer