Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- positive past medical history
- fever
- productive cough
- cavernous (amphoric) breath sounds
Other diagnostic factors
- cardiac murmur
- pleuritic chest pain
- constitutional symptoms
- cachexia
- pallor
- gingival disease
- halitosis
- absence of gag reflex
- dyspnea
- hemoptysis
- rigors
- weakness
- arthralgia
- hemorrhagic lesions
- inspiratory crackles
- bronchial breathing
- decreased breath sounds
- unilateral fixed rhonchus
Risk factors
- predisposition to aspiration of gastric contents
- poor dental hygiene and tooth extraction
- bronchial obstruction
- immunosuppression
- chronic illness
- extrapulmonary sepsis
- pneumonia
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- CBC
- chest x-ray
- sputum Gram stain
- sputum culture
- blood culture
- empyema fluid culture
Investigations to consider
- CT chest
- bronchoscopy
- quantitative cultures of protected specimen brushings
- quantitative cultures of protected bronchoalveolar lavage samples
- percutaneous needle aspiration and culture
- sputum cytology
- lung ultrasound
- echocardiogram
- rapid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for D-dimer
- multidetector CT thorax
- ventilation-perfusion scan
Treatment algorithm
low probability of gram-negative or multidrug resistant organism
high probability of gram-negative or multi-drug resistant organism
low probability of gram-negative or multidrug resistant organism
high probability of gram-negative or multidrug resistant organism: with or without penicillin/cephalosporin allergy
Contributors
Authors
Ioannis P. Kioumis, MD, PhD

Professor of Respiratory Medicine and Infectious Diseases
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Respiratory Failure Clinic
General Hospital G. Papanikolaou
Thessaloniki
Greece
Disclosures
IPK declares that he has no competing interests.
Georgia G. Pitsiou, MD, PhD

Professor of Respiratory Medicine
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Respiratory Failure Clinic
General Hospital G. Papanikolaou
Thessaloniki
Greece
Disclosures
GGP declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
William G. Cheadle, MD
Professor of Surgery
University of Louisville
Associate Chief of Staff for Research and Development
VAMC Louisville
Louisville
KY
Disclosures
WGC declares that he has no competing interests.
Nicholas Maskell, MD
Senior Lecturer and Consultant Physician
North Bristol Lung Centre
Southmead Hospital
Bristol
UK
Disclosures
NM declares that he has no competing interests.
Najib Rahman, BM, BCh, MA (Oxon), MRCP (UK)
MRC Training Fellow and Specialist Registrar, Respiratory Medicine
Oxford Centre for Respiratory Medicine
Churchill Hospital
Oxford
UK
Disclosures
NR declares that he has no competing interests.
Philip W. Ind, BA (Cantab), MB BChir, MA (Cantab), FRCP
Consultant Physician
Honorary Senior Lecturer
Imperial College Healthcare Trust
Hammersmith Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
PWI declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Walters J, Foley N, Molyneux M. Continuing education in anaesthesia, critical care and pain: pus in the thorax: management of empyema and lung abscess. 2011 Dec 1;11(6):229-33.Full text
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: radiologic management of infected fluid collections. 2019 [internet publication].Full text
American College of Radiology; Society of Interventional Radiology; Society for Pediatric Radiology. ACR-SIR-SPR practice guideline for specifications and performance of image-guided percutaneous drainage/aspiration of abscesses and fluid collections (PDAFC). 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
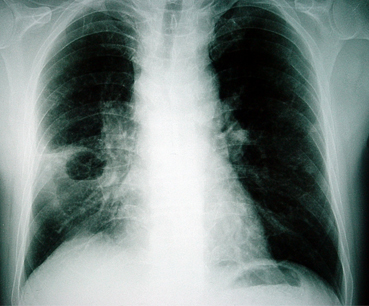
Differentials
- Neoplasm (primary or metastatic lung cancer, lymphoma)
- Tuberculosis
- Necrotizing pneumonia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Practice guideline for specifications and performance of image-guided percutaneous drainage/aspiration of abscesses and fluid collections (PDAFC)
- Appropriateness criteria: radiologic management of infected fluid collections
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer