Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- pruritus
- xerosis (dry skin)
- sites of skin involvement
Other diagnostic factors
- erythema
- scaling
- vesicles
- papules
- keratosis pilaris
- excoriations
- lichenification
- hypopigmentation
Risk factors
- filaggrin gene mutation
- age <5 years
- family history of atopic dermatitis
- allergic rhinitis
- asthma
- active and passive exposure to smoke
- female sex
- African-American ethnicity
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- clinical diagnosis
Tests to avoid
- IgG testing
- radioallergosorbent test
Investigations to consider
- IgE levels
- skin-prick testing
- oral food challenge
- trial elimination diet
- patch testing
- skin biopsy
Treatment algorithm
acute flare
chronic or relapsing disease
Contributors
Authors
Adelaide A. Hebert, MD
Professor & Director of Pediatric Dermatology
Clinical Specialist
Department of Dermatology and Pediatrics
University of Texas Health Sciences Center at Houston
Houston
TX
Divulgaciones
AAH has received research grants paid to UTHealth McGovern Medical School Houston from Pfizer, GSK, Dermavant, Arcutis, and Novan; has received honoraria from Pfizer, Verrica, and Novan; and is on the data safety monitoring boards for GSK, Ortho Dermatologics, and Regeneron-Sanofi.
Alexander Jafari, MD
Dermatology Clinical Research Fellow
Department of Dermatology
University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
Houston
TX
Divulgaciones
AJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Matthew Dallo, MD
Clinical Research Fellow
Department of Dermatology
University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
Houston
TX
Divulgaciones
MD declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimientos
Dr Adelaide A. Hebert, Dr Alexander Jafari, and Dr Matthew Dallo would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Eugenio G. Galindo, Dr Quoc-Bao D. Nguyen, Dr Mary D. DarConte, Dr Christina M. Gelbard, and Dr Daniel A. Grabella, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
EGG, QBDN, MDD, CMG, and DAG declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Amor Khachemoune, MD
Assistant Professor
New York University School of Medicine
NY
Disclosures
AK declares that he has no competing interests.
John English, MBBS, FRCP
Consultant Dermatologist
Department of Dermatology
Queen's Medical Centre
Nottingham University Hospitals
Nottingham
UK
Disclosures
JE declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management. Sep 2025 [internet publication].Full text
European Dermatology Forum. Living EuroGuiDerm guideline for the systemic treatment of atopic eczema. Oct 2023 [internet publication].Full text
Davis DMR, Drucker AM, Alikhan A, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with phototherapy and systemic therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024 Feb;90(2):e43-56.Full text Abstract
Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023 Jan 11:S0190-9622(23)00004-X.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
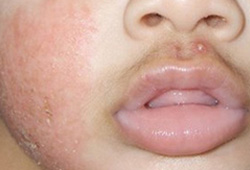
Differentials
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Allergic contact dermatitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management
- Atopic eczema in under 12s: diagnosis and management
More GuidelinesPatient information
Eczema
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer