Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of coronary artery disease
- history of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- history of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- presence of other known causes
- asymptomatic presentation
- tachycardia
Other diagnostic factors
- palpitations
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- presyncope
- syncope
Risk factors
- coronary artery disease
- left ventricular systolic dysfunction
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- long QT syndrome
- Brugada syndrome
- electrolyte imbalance
- drug toxicity
- Chagas disease and other cardiomyopathies
- sleep-disordered breathing
- catecholaminergic polymorphic VT
- family history of sudden death
- mental or physical stress
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- ECG
- electrolyte panel
- troponin
- CK-MB
Investigations to consider
- 24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring
- echocardiogram
- cardiac catheterization
- cardiac MRI with gadolinium
- electrophysiologic testing
- stress testing
- genetic screening
Treatment algorithm
no cardiac comorbidity: asymptomatic and ≤10% NSVT/premature ventricular contraction (PVC) burden
no cardiac comorbidity: symptomatic NSVT or >10% asymptomatic NSVT/premature ventricular contraction (PVC) burden
chronic coronary artery disease (CAD)
post-myocardial infarction (MI)
idiopathic dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Contributors
Authors
Fred Kusumoto, MD

Professor of Medicine
Mayo Medical School
Division of Cardiovascular Diseases
Department of Medicine
Mayo Clinic Florida
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
FK declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Professor Kusumoto would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ronald R. Butendieck Jr, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
RRB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Timothy Markman, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
TM declares that he has no competing interests.
Vias Markides, MB(Hons), BS(Hons), MD, FRCP
Consultant Cardiologist and Chair
Arrhythmias
Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Trust
Hon. Senior Lecturer
Imperial College
London
UK
Disclosures
VM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Al-Khatib SM, Stevenson WG, Ackerman MJ, et al. 2017 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 2018 Sep 25;138(13):e272-e391.Full text Abstract
Zeppenfeld K, Tfelt-Hansen J, de Riva M, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Eur Heart J. 2022 Oct 21;43(40):3997-4126.Full text Abstract
Katritsis DG, Zareba W, Camm AJ. Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Nov 13;60(20):1993-2004.Full text Abstract
Goldberger JJ, Cain ME, Hohnloser SH, et al. American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Rhythm Society scientific statement on noninvasive risk stratification techniques for identifying patients at risk for sudden cardiac death: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology Committee on Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2008 Sep 30;118(14):1497-1518. Abstract
Epstein AE, DiMarco JP, Ellenbogen KA, et al. ACC/AHA/HRS 2008 guidelines for device-based therapy of cardiac rhythm abnormalities: executive summary. Circulation. 2008 Jun;117(6):e350-408.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
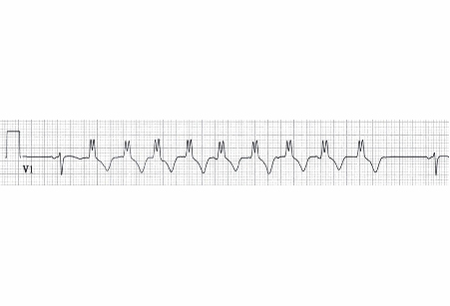
Differentials
- SVT with aberrant conduction
- Electrical artifact
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2022 ESC guideline for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death
- 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure
More GuidelinesPatient information
Heart attack
Heart attack: what is it?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer