Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- numbness
- weakness
- pain
- sicca symptoms
- parotid gland enlargement
- rash, ulcerations, or pigment changes
- wheeze, cough, other pulmonary signs
- fever, night sweats, weight loss, and malaise
Other diagnostic factors
- predisposing conditions causing vasculitis, inflammation, or other nerve damage
Risk factors
- age over 50 years
- sarcoidosis
- hepatitis C
- cryoglobulinemia
- hepatitis B
- connective tissue disease
- livedo reticularis
- primary vasculitis
- medications
- HIV infection
- non-HIV, non-hepatitis infections
- severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection
- recreational drug use
- genetic predisposition
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- electromyogram (EMG)
- CBC with differential
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- serum creatinine
- serum glucose
- cryoglobulins
- serum complement
- hepatitis B surface antigen
- hepatitis C antibodies or RNA
- anti-HIV antigens or HIV RNA
- Lyme disease antibodies
- cytoplasmic and perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (c-ANCA and p-ANCA)
- rheumatoid factor
- antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
- anti-double-stranded (ds) DNA
- anti-Sjogren syndrome-related antigen A (SSA) or -SSB antibodies
- serum angiotensin-converting enzyme
- protein electrophoresis and immunofixation
- chest x-ray
- urinalysis
- muscle and nerve biopsy
Tests to consider
- anti-Smith (anti-Sm) antibodies
- anti-topoisomerase I (anti-Scl 70) and anti-centromere (ACA) antibodies
- skin biopsy
- lip biopsy
- anti-Hu antibodies
- cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analyses
- CT of chest, abdomen/pelvis
- positron emission tomography (PET) scan of chest, abdomen, or pelvis
- conventional angiography
- magnetic resonance angiography
Treatment algorithm
primary systemic or nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathies: initial presentation
secondary vasculitic neuropathies: initial presentation
vasculitis in remission
Contributors
Authors
Ashok Verma, MD, DM, MBA, FAAN, FANA
Professor of Neurology
Director, Neuromuscular Medicine Fellowship Training Program
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Don Soffer Clinical Research Center
Miami
FL
Disclosures
AV declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Professor Ashok Verma would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Kevin Scott, Dr Milind Kothari, and Dr Jenice Robinson, the previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
JR, KS, and MK declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
John J. Kelly, MD
Professor and Chairman
Department of Neurology
The George Washington University Medical Center
Washington
DC
Disclosures
JJK declares that he has no competing interests.
Cory Toth, BSc, MD, FRCP(C)
Assistant Professor of Neurosciences
Hotchkiss Brain Institute
University of Calgary
Alberta
Canada
Disclosures
CT declares that he has no competing interests.
Jeremy Bland, FRCP
Consultant Neurophysiologist
East Kent Hospitals NHS Trust
Canterbury
Kings College Hospital NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
JB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Graf J, Imboden J. Vasculitis and peripheral neuropathy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019 Jan;31(1):40-5. Abstract
Beachy N, Satkowiak K, Gwathmey KG. Vasculitic neuropathies. Semin Neurol. 2019 Oct;39(5):608-19. Abstract
Collins MP, Hadden RD. The nonsystemic vasculitic neuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017 Apr;13(5):302-16.Full text Abstract
Hellmich B, Sanchez-Alamo B, Schirmer JH, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Mar [Epub ahead of print].Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
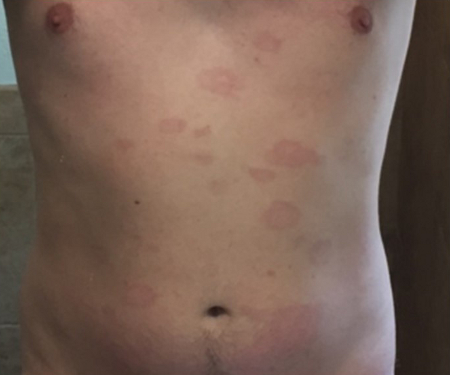
Differentials
- Diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy
- Multiple compression/entrapment mononeuropathies
- Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update
- European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on diagnosis and treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer