Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- bowel sounds in chest
Other diagnostic factors
- heartburn
- regurgitation
- obesity
- chest pain
- dysphagia
- odynophagia
- hematemesis
- shortness of breath
- cough
- oropharyngitis
- wheezing
- nonbilious vomiting
- fever and chills
- confusion
Risk factors
- obesity
- increased age
- previous gastroesophageal procedure
- elevated intra-abdominal pressure
- male sex
- incisional, umbilical, or inguinal hernia
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
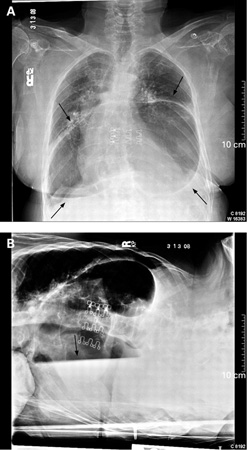
- chest x-ray
- upper gastrointestinal fluoroscopy with oral contrast
Tests to consider
- esophago-gastro-duodenoscopy
- CT scan or MRI scan
- high-resolution esophageal manometry and pH monitoring
Treatment algorithm
upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and/or obstruction and/or volvulus
irreversible organ ischemia and/or necrosis
symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
type I refractory to medical therapy or patient prefers surgery
types II, III, and IV
Contributors
Authors
Constantine T. Frantzides, MD, PhD, FACS

Director
Chicago Institute of Minimally Invasive Surgery
St. Francis Hospital
Clinical Professor of Surgery
University of Illinois Chicago
Chicago
IL
Declarações
CTF declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Constantine T. Frantzides would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Mark A. Carlson, Dr Amy J. Hargrove and Dr Minh B. Luu, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
MAC, AJH and MBL declare they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Frank A. Granderath, MD
Associate Professor
Department of General, Visceral and Transplant Surgery
University Hospital Tuebingen
Germany
Declarações
FAG declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. Guidelines for the management of hiatal hernia. Apr 2013 [internet publication].Texto completo
Roman S, Kahrilas PJ. The diagnosis and management of hiatus hernia. BMJ. 2014 Oct 23;349:g6154. Resumo
Sfara A, Dumitrascu DL. The management of hiatal hernia: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Med Pharm Rep. 2019 Oct;92(4):321-25.Texto completo Resumo
Antoniou SA, Müller-Stich BP, Antoniou GA, et al. Laparoscopic augmentation of the diaphragmatic hiatus with biologic mesh versus suture repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2015 Jul;400(5):577-83. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Angina pectoris
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Pneumonia
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Guidelines for the surgical treatment of hiatal hernias
- ACR appropriateness criteria: epigastric pain
Mais DiretrizesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer