Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- bruxism activities: teeth grinding/clenching, jaw bracing/thrusting
- oral parafunctions
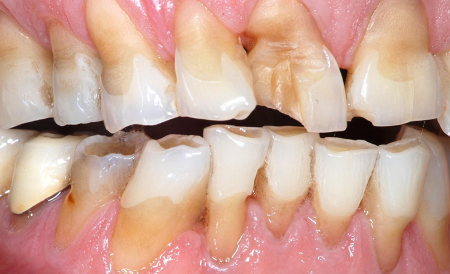
- tooth wear
- jaw muscle and/or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain
- jaw muscle tenderness
- stress and anxiety
- caffeine, smoking, or alcohol use
- history of sleep disorders
- selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor or dopamine antagonist use
- ecstasy or cocaine use
- jaw muscle hypertrophy
Other diagnostic factors
- headache
- tooth soreness and/or hypersensitivity
- history of temporomandibular disorder (TMD)
- dental restorations and/or implant failure
- periodontal problems
- tooth chippings, cracks, and fractures
- oral mucosal changes
Risk factors
- smoking, caffeine, alcohol consumption
- stress sensitivity and anxious personality traits
- snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, and other sleep disorders
- medication and illicit drug use
- genetic predisposition
- primary motor disorders
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- clinical diagnosis
- polysomnographic (PSG) study
Investigations to consider
- electromyography (EMG)
- ecological momentary assessment (EMA)
Treatment algorithm
awake bruxism
sleep bruxism
Contributors
Authors
Frank Lobbezoo, DDS, PhD
Professor, Chair, and Vice Dean
Department of Oral Health Sciences
Academic Centre for Dentistry Amsterdam (ACTA)
MOVE Research Institute Amsterdam
University of Amsterdam
VU University Amsterdam
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Disclosures
FL is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Daniele Manfredini, DDDS, PhD
Full Professor Oral Physiology and Gnathology
School of Dentistry
University of Siena
Siena
Italy
Disclosures
DM is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Alessandro Bracci, DDS
Associate Professor
School of Dentistry
Department of Neuroscience
University of Padua
Padua
Italy
Disclosures
AB is a shareholder for WMA Srl, whose products include BruxApp. AB is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Professor Daniele Manfredini, Professor Frank Lobbezoo, and Alessandro Bracci would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Peter Svensson, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
PS is chairman of the clinical advisory board and has received fees for consulting for Medotech, the manufacturer of GrindCare. PS is also an author of several references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Alan Glaros, PhD
Associate Dean and Professor
Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences
Kansas City
MO
Disclosures
AG is a member of the clinical advisory board of Medotech and has received GrindCare devices for evaluation. AG is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Lobbezoo F, Ahlberg J, Raphael KG, et al. International consensus on the assessment of bruxism: report of a work in progress. J Oral Rehabil. 2018 Nov;45(11):837-44.Full text Abstract
Raphael KG, Santiago V, Lobbezoo F. Is bruxism a disorder or a behaviour? Rethinking the international consensus on defining and grading of bruxism. J Oral Rehabil. 2016;43:791-8. Abstract
Manfredini D, Ahlberg J, Winocur E, et al. Management of sleep bruxism in adults: a qualitative systematic literature review. J Oral Rehabil. 2015;42:862-74. Abstract
Lobbezoo F, van der Zaag J, van Selms MK, et al. Principles for the management of bruxism. J Oral Rehabil. 2008 Jul;35(7):509-23. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Oromandibular dystonia
- Huntington disease
- Tourette syndrome
More DifferentialsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer