Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- low-grade fever
- oral vesicles and ulcers
- rash and/or vesicles on the hands and feet
Other diagnostic factors
- malaise
- sore mouth
- loss of appetite
- sore throat
- rash and/or vesicles on the buttocks
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- cough
- tongue erythema/edema
- arthralgia
Risk factors
- immunosuppression
- age <10 years
- family or school contacts with infection
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- viral culture
- CBC
Emerging tests
- PCR molecular assays
Treatment algorithm
all patients
Contributors
Authors
Malobi I. Ogboli, MBBS, FRCP
Consultant Dermatologist
Birmingham Children's Hospital and Birmingham City Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
MIO declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Helen Goodyear, MBChB, MRCP, FRCPCH, MD, MMed
Consultant Paediatrician
Heartlands Hospital
Birmingham
UK
Disclosures
HG declares that she has no competing interests.
Andrew Riordan, MD, FRCPCH, MRCP, DTM&H
Consultant in Paediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology
Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital (Alder Hey)
Liverpool
UK
Disclosures
AR declares that he has no competing interests.
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
University of California
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
DC declares that he has no competing interests.
Leonid Izikson, MD
Staff Dermatologist
Department of Dermatology
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston
MA
Disclosures
LI declares that he has no competing interests.
Aisha Sethi, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Associate Residency Program Director
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
AS declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Alsop J, Flewett TH, Foster JR. "Hand-foot-and-mouth disease" in Birmingham in 1959. Br Med J. 1960;2:1708-1711.Full text Abstract
Ishimaru Y, Nakano S, Yamaoka K, et al. Outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease by enterovirus 71. High incidence of complication disorders of central nervous system. Arch Dis Child. 1980;55:583-588.Full text Abstract
Saguil A, Kane SF, Lauters R, et al. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: rapid evidence review. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Oct 1;100(7):408-14.Full text Abstract
Chang LY, Tsao KC, Hsia SH, et al. Transmission and clinical features of enterovirus 71 infections in household contacts in Taiwan. JAMA. 2004;291:222-227.Full text Abstract
Chang LY, Lin TY, Huang YC, et al. Comparison of enterovirus 71 and coxsackie-virus A16 clinical illnesses during the Taiwan enterovirus epidemic, 1998. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999;18:1092-1096. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
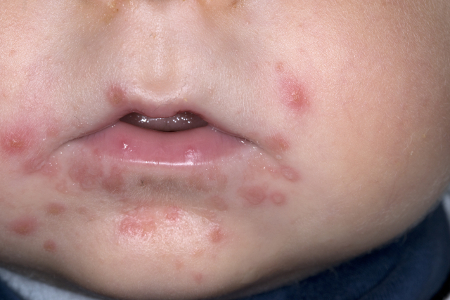
Differentials
- Aphthous stomatitis or oral aphthous ulcers
- Herpes simplex
- Herpangina
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- A guide to clinical management and public health response for hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD)
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer