Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- family history
- epilepsy
- cardiac rhabdomyoma (single or multiple)
- renal angiomyolipomas
- lymphangioleiomyomatosis of the lung
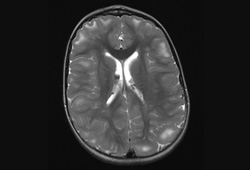
- cerebral subependymal calcified nodules
- multiple cortical tubers and/or radial migration lines
- giant cell astrocytoma
- facial angiofibromas
- cephalic plaque(s)
- nontraumatic ungual or periungual fibromas
- hypomelanotic macules
- shagreen patch(es) (connective tissue nevus)
- retinal nodular hamartoma(s)
- polycystic kidney disease
Other diagnostic factors
- numerous dental enamel pits and intraoral fibromas
- autism
- cognitive impairment
- behavioral problems
- multiple hamartomatous colonic polyps
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- genetic testing
- brain MRI
- neurodevelopmental assessment
- electroencephalogram (EEG)
- ECG
- echocardiography
- abdominal MRI
- glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- blood pressure
- high-resolution chest CT
- pulmonary function tests and 6-minute walk test
- skeletal x-ray
- colonoscopy
- renal biopsy
Treatment algorithm
renal cell carcinoma (suspected or confirmed)
intracranial aneurysm
neurologic
skin lesions
renal
cardiovascular
pulmonary
cognitive and behavioral
Contributors
Authors
Francis J. DiMario Jr, MD, MA, FAAP
Professor of Pediatrics and Neurology
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Associate Chair for Academic Affairs and Faculty Development
Department of Pediatrics
Academic Chief Emeritus
Division of Pediatric Neurology
Connecticut Children's Medical Center
Hartford
CT
Disclosures
FJD is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Robert Robinson, MBBS, MA, MRCP, PhD
Consultant Paediatric Neurologist
Great Ormond Street Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
RR declares that he has no competing interests.
David Neal Franz, MD
Professor of Pediatrics and Neurology
Director
Tuberous Sclerosis Clinic
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati
OH
Disclosures
DNF declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Northrup H, Aronow ME, Bebin EM, et al. Updated international tuberous sclerosis complex diagnostic criteria and surveillance and management recommendations. Pediatr Neurol. 2021 Oct;123:50-66.Full text Abstract
Caban C, Khan N, Hasbani DM, et al. Genetics of tuberous sclerosis complex: implications for clinical practice. Appl Clin Genet. 2016 Dec 21;10:1-8.Full text Abstract
Amin S, Kingswood JC, Bolton PF, et al. The UK guidelines for management and surveillance of tuberous sclerosis complex. QJM. 2019 Mar 1;112(3):171-82.Full text Abstract
de Vries PJ, Whittemore VH, Leclezio L, et al. Tuberous sclerosis associated neuropsychiatric disorders (TAND) and the TAND Checklist. Pediatr Neurol. 2015 Jan;52(1):25-35.Full text Abstract
Li M, Zhou Y, Chen C, et al. Efficacy and safety of mTOR inhibitors (rapamycin and its analogues) for tuberous sclerosis complex: a meta-analysis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019 Feb 13;14(1):39.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH)
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN-1)
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Updated international tuberous sclerosis complex diagnostic criteria and surveillance and management recommendations
- Updated international tuberous sclerosis complex diagnostic criteria and surveillance and management recommendations
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer