Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- vaginal protrusion/bulge
- sensation of vaginal pressure
Other diagnostic factors
- urinary incontinence
- defecatory dysfunction
- pelvic pain
- voiding dysfunction
- sexual dysfunction
Risk factors
- vaginal delivery
- advancing age
- obesity
- previous surgery for prolapse
- genetic factors
- white ancestry
- connective tissue disorders
- increased intra-abdominal pressure
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- assessment of postvoid residual urine (PVR) volume
- urinalysis
Tests to consider
- urodynamics
Treatment algorithm
asymptomatic
symptomatic
Contributors
Authors
Lior Lowenstein, MD, MS, MHA, MBA

Associate Clinical Professor and Head of Gynecology Division
Rambam Health Care Campus
Rappaport Faculty of Medicine
Technion-Israel Institute of Technology
Haifa
Israel
Disclosures
LL declares that he has no competing interests.
Omer Anis, MD
Urology Department
Chaim-Sheba Medical Center
Tel Aviv
Israel
Disclosures
OA declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Lior Lowenstein and Dr Omer Anis would like to thank Dr Linda Brubaker, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
LB has received editorial honoraria from JAMA, UpToDate, and the Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery journal. LB is an author of some of the references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Sarah Collins, MD
Associate Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Northwestern University
Feinberg School of Medicine
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
SC declares that she has no competing interests.
Sushma Srikrishna, MRCOG
Locum Consultant Urogynaecologist and Obstetrician
Kings College Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
SS declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Practice bulletin no. 214: pelvic organ prolapse. Nov 2019 [internet publication].Full text
Winters JC, Dmochowski RR, Goldman HB, et al; American Urological Association; Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction. Urodynamic studies in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. J Urol. 2012 Dec;188(6 Suppl):2464-72. Abstract
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management. Jun 2019 [internet publication].Full text
Maher C, Feiner B, Baessler K, et al. Surgery for women with anterior compartment prolapse. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 30;(11):CD004014.Full text Abstract
Baessler K, Christmann-Schmid C, Maher C, et al. Surgery for women with pelvic organ prolapse with or without stress urinary incontinence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 19;(8):CD013108.Full text Abstract
Brubaker L, Cundiff GW, Fine P, et al; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Abdominal sacrocolpopexy with Burch colposuspension to reduce urinary stress incontinence. N Engl J Med. 2006 Apr 13;354(15):1557-66.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
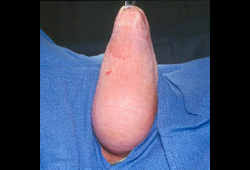
Differentials
- Cervical elongation
- Vaginal cyst
- Gynecologic cancer
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Non-neurogenic female LUTS
- AAGL practice report: practice guidelines on the prevention of apical prolapse at the time of benign hysterectomy
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer