Summary
Definition
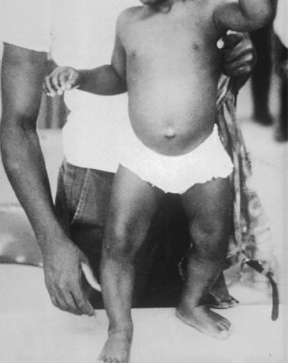
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of breast-feeding
- history of inadequate sunlight exposure
- history of calcium deficiency
- history of phosphate deficiency
Other diagnostic factors
- bone pain
- growth faltering
- delayed achievement of motor milestones
- bony deformities
- muscle weakness
- carpopedal spasm
- tetany
- numbness or paresthesias
- hypocalcemic seizures
Risk factors
- age 6 to 23 months
- inadequate sunlight exposure
- breast-feeding
- darker skin complexion
- calcium deficiency
- phosphate deficiency
- family history of rickets
- antacids, loop diuretics, corticosteroids, or anticonvulsants
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- radiograph of a long bone
- serum calcium
- serum inorganic phosphorus
- serum parathyroid hormone level
- 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (calcidiol)
- alkaline phosphatase and liver function tests
- serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen
- urinary calcium and phosphorus
Tests to consider
- 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels (calcitriol)
Treatment algorithm
symptomatic hypocalcemia
calcium-deficient rickets: vitamin D deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: calcium deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: pseudovitamin D deficiency
calcium-deficient rickets: vitamin D resistance
hypophosphatemic rickets: X-linked
hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria
hypophosphatemic rickets: tumor-induced
Contributors
Authors
Carlos Palacio, MD, MPH, FACP

Professor of Medicine
Associate Program Director
Internal Medicine Residency
Department of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
CP declares that he has no competing interests.
Firas Warda, MD
Endocrinology Fellow
Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
Department of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
FW declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Professor Carols Palacio and Dr Firas Warda would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Robert Olney, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
RO declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Phil Fischer, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Disclosures
PF declares that he has no competing interests.
Zulf Mughal, MD
Consultant in Paediatric Bone Disorders
Department of Paediatric Endocrinology
Royal Manchester Children's Hospital
UK
Disclosures
No disclosures
Arshag Mooradian, MD
Professor of Medicine
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville
FL
Disclosures
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG committee opinion no. 495: vitamin D: screening and supplementation during pregnancy. Jul 2011 [internet publication].Full text
Munns CF, Shaw N, Kiely M, et al. Global consensus recommendations on prevention and management of nutritional rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Feb;101(2):394-415.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Hypophosphatasia
- Metaphyseal dysostoses
- Blount syndrome
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Rickets: standard treatment guidelines
- Global consensus recommendations on prevention and management of nutritional rickets
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer