Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- anogenital ulcer
- lymphadenopathy
- diffuse rash
- constitutional symptoms
- fatigue
- rhinitis (congenital syphilis)
- hepatosplenomegaly (congenital syphilis)
- patchy alopecia
- condylomata lata
- memory impairment, altered mood, confusion, or dementia
- visual changes
- Argyll-Robertson pupils
- loss of sense of vibration, proprioception, and position sense
- ataxia
- loss of anal and bladder sphincter control
- positive Romberg sign
- diastolic murmur
- rubbery lesions/nodules with a necrotic center
- miscarriage, stillbirth, or neonatal death (congenital syphilis)
- premature labor and intrauterine growth retardation (congenital syphilis)
- neonatal skin rash (congenital syphilis)
- tibial bowing (congenital syphilis)
- craniofacial malformation (congenital syphilis)
- tooth abnormalities (congenital syphilis)
- necrotizing funisitis (congenital syphilis)
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- mouth ulcer
- asymptomatic with positive serology (latent syphilis)
- tremor
- headache
- meningismus
- eye pain
- hearing loss
- seizures
- peripheral edema
- jaundice
- peripheral neuropathy
- areflexia
- angina
- dyspnea
- organomegaly
- skin or visceral organ perforation or collapse of structure
- neonatal neurologic abnormalities (congenital syphilis)
Factores de riesgo
- sexual contact with an infected person
- men who have sex with men (MSM)
- illicit drug use
- commercial sex workers
- multiple sexual partners
- people with HIV or other STIs
- syphilis during pregnancy (risk for congenital syphilis)
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- dark-field microscopy of swab from lesion
- serum treponemal enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
- chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA)
- serum Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TPPA)
- serum Treponema pallidum hemagglutination (TPHA)
- serum Treponema pallidum latex agglutination (TPLA)
- serum fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) test
- immunocapture assay
- line immunoassay (LIA) serologic test
- serum rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
- serum Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- lumbar puncture, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis
- CXR
- echocardiogram
- CT brain
- MRI brain
- HIV test
- fetal ultrasound scan
- CBC
- long-bone x-rays
- liver function tests (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase) and bilirubin
- auditory brainstem response
- audiometry
- fetal skeletal survey
Pruebas emergentes
- Treponema pallidum polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (sample taken directly from ulcerative lesions)
- point of care (POC) testing with either treponemal or combination treponemal/nontreponemal antibody
Algoritmo de tratamiento
adults with suspected early infection or sexual contacts of patients with confirmed infection
adults without neurosyphilis
adults with neurosyphilis
congenital syphilis
Colaboradores
Autores
Juan C. Salazar, MD, MPH, FAAP
Professor and Chair
Department of Pediatrics
University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Physician in Chief
Connecticut Children’s
Hartford
CT
Divulgaciones
JCS has received NIH funding for syphilis research. JCS has been invited to speak about syphilis and congenital syphilis at various international conferences. He has been the principal author, corresponding author and/or co-author of several papers in the field of syphilis vaccine development, syphilis molecular epidemiology, and syphilis pathogenesis. JCS is the author of references cited in this topic.
Agradecimientos
Dr Juan C. Salazar would like to gratefully acknowledge Adriana R. Cruz, Jairo M. Montezuma-Rusca, Nicholas Bennett, Patrick French, and Nooshin Barmania, previous contributors to this topic. We would also like to acknowledge our infectious diseases expert panel member, Dr Elisabeth Adderson, for her contribution to this topic.
Divulgaciones
PF is an author of a reference cited in this topic. EA, ARC, JMMR, NB, and NB declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Robert A. Larsen, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of Southern California
Keck School of Medicine
Los Angeles
CA
Divulgaciones
RAL declares that he has no competing interests.
William Rodriguez, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Harvard Medical School
Director of Research
Global Health Delivery Project
Harvard School of Public Health
Boston
MA
Divulgaciones
WR declares that he has no competing interests.
Jennifer Handforth, MB ChB, MRCPCH, DTM&H
Consultant Paediatrician
Croydon University Hospital
Croydon
UK
Divulgaciones
JH declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Stoltey JE, Cohen SE. Syphilis transmission: a review of the current evidence. Sex Health. 2015 Apr;12(2):103-9.Texto completo Resumen
Kingston M, Apea V, Evans C, et al. BASHH UK guidelines for the management of syphilis 2024. Int J STD AIDS. 2024 Dec;35(14):1142-60.Texto completo Resumen
World Health Organization. Guidelines for the treatment of Treponema pallidum (syphilis). 2016 [internet publication].Texto completo
Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Jul 23;70(4):1-187.Texto completo Resumen
World Health Organization. WHO guideline on syphilis screening and treatment for pregnant women. 2017 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
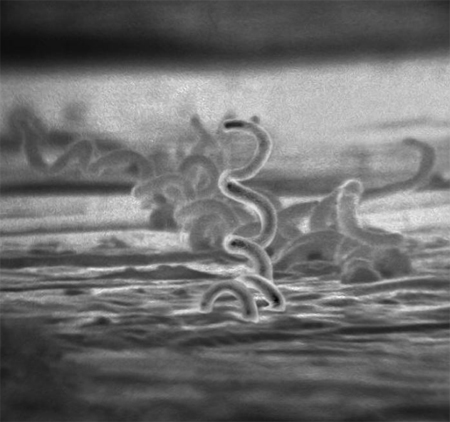
Diferenciales
- Genital herpes
- Chancroid
- Primary HIV infection
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- BASHH UK guidelines for the management of syphilis in pregnancy and children 2024
- BASHH UK guidelines on the management of syphilis 2024
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Syphilis: what is it?
Syphilis: how is it diagnosed and treated?
Más Folletos para el pacienteVideos
Diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults: animated demonstration
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
Más vídeosInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad