Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- black or Hispanic ancestry
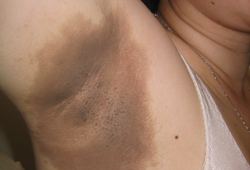
- new pigmented velvety skin lesions in axillary or flexural areas
- lesions distributed on the posterior neck, axillae, vulva, umbilicus, inner thighs, and groin
- weight gain
- generalized distribution
- sudden appearance of multiple seborrheic keratoses
Other diagnostic factors
- age >40 years
- child/young adult
- female sex
- acrochordons (skin tags)
- acral distribution
- pruritus
- mucosal or palmoplantar lesions
- weight loss
Risk factors
- obesity
- insulin resistance
- positive family history of AN or genetic syndrome
- family history of diabetes mellitus
- malignancy
- medication
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- fasting blood glucose
- fasting blood insulin
- abdominal CT
- skin biopsy
Treatment algorithm
initial presentation with underlying cause
unresolved despite treatment of underlying cause, or hereditary or idiopathic
Contributors
Authors
David S. Cassarino, MD, PhD
Consultant Dermatopathologist
Southern California Permanente Medical Group
Sunset Medical Center
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
DSC declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr David Cassarino would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Laura Westerling for her contribution to this topic. LNW declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Christine Ko, MD
Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Department of Dermatology
Yale University
New Haven
CT
利益声明
CK declares that she has no competing interests.
John English, MBBS, FRCP
Consultant Dermatologist
Department of Dermatology
Queen's Medical Centre
Nottingham University Hospitals
Nottingham
UK
利益声明
JE declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
参考文献
关键文献
Das A, Datta D, Kassir M, et al. Acanthosis nigricans: a review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Aug;19(8):1857-65. 摘要
Schwartz RA. Acanthosis nigricans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994 Jul;31(1):1-19. 摘要
Patel NU, Roach C, Alinia H, et al. Current treatment options for acanthosis nigricans. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018 Aug 7:11:407-13.全文 摘要
参考文献
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
鉴别诊断
- Epidermal nevus
- Dowling-Degos disease (reticular pigmented flexural anomaly)
- Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis (of Gougerot and Carteaud)
更多 鉴别诊断登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明