Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea
- infertility
- galactorrhea
- loss of sexual desire (libido)
- erectile dysfunction
- visual deterioration (e.g., temporal hemianopia)
Other diagnostic factors
- osteoporosis
- ophthalmoplegia
- headaches
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition (e.g., presence of mutation resulting in multiple endocrine neoplasia-1 [MEN-1], familial isolated pituitary adenoma [FIPA])
- estrogen therapy
- male sex, 30 to 60 years of age
- female sex, 20 to 50 years of age
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- serum prolactin
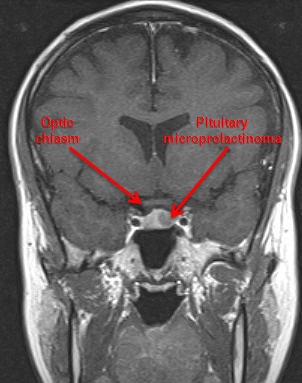
- pituitary MRI
- computerized visual-field examination
Treatment algorithm
premenopausal women
postmenopausal women
men
Contributors
Authors
Niamh Martin, MB ChB, PhD, FRCP
Reader in Endocrinology
Imperial Centre for Endocrinology
Department of Metabolism, Digestion and Reproduction
Imperial College London
London
UK
Disclosures
NM declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Niamh Martin would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Ilan Shimon, the previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
IS receives consultancy and lecturing fees from Pfizer, Israel, and is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Mark Molitch, MD
Professor
Division of Endocrinology
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
MM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
References
Key articles
Wildemberg LE, Fialho C, Gadelha MR. Prolactinomas. Presse Med. 2021 Dec;50(4):104080.Full text Abstract
Melmed S, Casanueva FF, Hoffman AR, et al; Endocrine Society. Diagnosis and treatment of hyperprolactinemia: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Feb;96(2):273-88.Full text Abstract
Xia MY, Lou XH, Lin SJ, et al. Optimal timing of dopamine agonist withdrawal in patients with hyperprolactinemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2018 Jan;59(1):50-61. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Nonfunctioning pituitary macroadenomas
- Drug-induced hyperprolactinemia
- Primary hypothyroidism
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: neuroendocrine imaging
- Clinical practice guidelines for the management of aggressive pituitary tumours and carcinomas
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer