Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- presence of risk factors
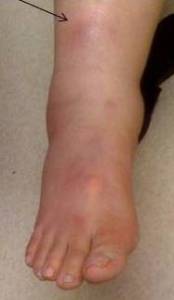
- nodules on shins
- uveitis, red eyes, retinal nodules, or candle-wax drippings
- nodules on other skin areas
- anaesthetic skin lesions
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- joint pains
- fever
- diarrhoea, constipation, abdominal pain, haematochezia
- enlarged spleen
- miliary nodules on the retina
Factores de riesgo
- streptococcal infection
- sarcoidosis
- tuberculosis
- coccidioidomycosis
- histoplasmosis
- blastomycosis
- brucellosis
- Behcet's disease
- oral contraceptives
- sulfonamides
- iodides and anti-epileptic drugs
- psittacosis
- leprosy
- inflammatory bowel disease
- pregnancy
- malignancy
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- FBC
- anti-streptolysin-O titre
- chest x-ray
- tuberculin skin test, interferon gamma release assay
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- serum ACE level
- skin lesion biopsy
- coccidioidin skin test
- histoplasmin skin test
- lepromin skin test
- blastomycosis serology
- brucellosis serology
- psittacosis serology
- x-ray symptomatic joints
- rheumatoid factor testing
- Yersinia agglutination titre
- Yersinia stool cultures
- colonoscopy
- serum IgD
- deep punch biopsies including subcutaneous fat, or incisional biopsies
Algoritmo de tratamiento
mild to moderately severe symptoms
severe refractory symptoms
Colaboradores
Autores
Daniela Kroshinsky, MD, MPH

Associate Professor of Dermatology
Harvard Medical School
Director of Pediatric Dermatology
Director of Inpatient Dermatology
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston
MA
Divulgaciones
DK declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimientos
Dr Daniela Kroshinsky would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Om P. Sharma, a previous contributor to this topic. Dr Kroshinsky would also like to thank Priyanka Vedak for her contribution to this topic. We would like to gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the late Elisabeth Higgins (Consultant Dermatologist, King’s College Hospital) for her peer review of this topic.
Divulgaciones
OPS declared that he had no competing interests. PV declared that she had no competing interests. EH declared that she had no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Robert T. Brodell, MD
Professor of Internal Medicine
Clinical Professor of Dermatopathology
Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine
Warren
Associate Clinical Professor of Dermatology
Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
Cleveland
OH
Divulgaciones
RTB declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Bondi EE, Margolis DJ, Lazarus ZS. Panniculitis. In: Freedberg I, Eisen A, Wolff K, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 5th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 1999: 1284-6.
Requena L, Requena C. Erythema nodosum (review). Dermatol Online J. 2002 Jun;8(1):4. Resumen
Sterling JB, Heymann WR. Potassium iodide in dermatology: a 19th century drug for the 21st century-uses, pharmacology, adverse effects, and contraindications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000 Oct;43(4):691-7. Resumen
Friedman ES, LaNatra N, Stiller MJ. NSAIDs in dermatologic therapy: review and preview. J Cutan Med Surg. 2002 Sep-Oct;6(5):449-59. Resumen
Schultz E, Whiting D. Treatment of erythema nodosum and nodular vasculitis with potassium iodides. Br J Dermatol. 1976 Jan;94(1):75-8. Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Weber-Christian disease
- Alpha-1-anti-trypsin deficiency
- Nodular vasculitis (erythema induratum or Bazin's disease)
Más DifferentialsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
