Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
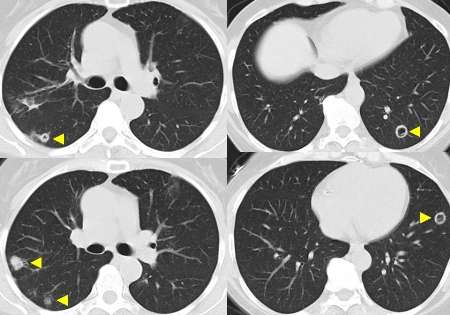
- upper and lower respiratory tract involvement
- renal involvement
- constitutional features
Other diagnostic factors
- ocular manifestations
- cutaneous manifestations
- musculoskeletal manifestations
- neurologic manifestations
- signs or symptoms of thromboembolism
- gastrointestinal involvement
- cardiac involvement
- breast mass
- lower genitourinary tract involvement
- endocrine involvement
- isolated mass lesions/focal granuloma
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition
- infection
- environmental exposures
- white ethnicity
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- urinalysis and microscopy
- CT chest
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)
- CBC and differential
- serum creatinine
- C-reactive protein
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- liver function tests
- serum calcium
Tests to consider
- tissue biopsy
- pulmonary function testing
- bronchoscopy
- electromyography/nerve conduction studies
- upper airway endoscopy
- CT sinuses
Treatment algorithm
severe (life/organ-threatening) disease: remission induction
nonsevere (non-life/organ-threatening) disease: remission induction
remission successfully induced
relapse following successful remission
Contributors
Authors
Eamonn Molloy, MD, MS, FRCPI
Consultant Rheumatologist
Department of Rheumatology
St Vincent's University Hospital
Dublin
Ireland
Disclosures
EM declares that he has been a speaker for, and participated in advisory board for Abbvie, Janssen, Gilead, Novartis. He has received sponsorship to attend conferences from Abbvie, Janssen and UCB, and received research funding from Abbvie.
Peer reviewers
Curry L. Koening, MD, MS
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Rheumatology Division
University of Utah School of Medicine
Salt Lake City
UT
Disclosures
CLK declares that he has no competing interests.
Jaap M. van Laar, MD, PhD
Professor of Clinical Rheumatology
Musculoskeletal Research Group
Institute of Cellular Medicine
Newcastle University
The Medical School
Newcastle upon Tyne
UK
Disclosures
JMVL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Chung SA, Langford CA, Maz M, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation guideline for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Aug;73(8):1088-105.Full text Abstract
Hellmich B, Sanchez-Alamo B, Schirmer JH, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Mar 16:ard-2022-223764.Full text Abstract
Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, et al; RAVE-ITN Research Group. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):221-32.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA, Churg-Strauss syndrome)
- Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA)
- Classic polyarteritis nodosa (cPAN)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the management of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitis
- Guideline for vaccinations in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease
More GuidelinesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal