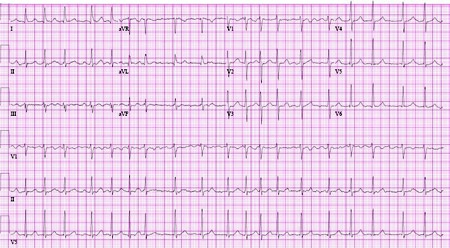
Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- worsening heart failure or pulmonary symptoms
- jugular venous pulsations with rapid flutter waves
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- palpitations
- fatigue or lightheadedness
- chest pain
- dyspnea
- syncope
- hypotension
- embolic events
Factores de riesgo
- increasing age
- valvular dysfunction
- atrial septal defects
- atrial dilation
- recent cardiac or thoracic procedures
- surgical or postablation scarring of atria
- heart failure
- hyperthyroidism
- COPD
- asthma
- pneumonia
- antiarrhythmic drugs for atrial fibrillation
- diabetes
- digitalis use
- male sex
- congenital or lone atrial flutter
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- ECG
- thyroid function tests
- serum electrolytes
Tests to avoid
- imaging stress tests
- coronary CT angiography
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- pulmonary function tests
- CXR
- digitalis level
- cardiac enzymes
- spiral CT with pulmonary embolism protocol
- transthoracic echocardiogram
- atrial electrogram recording
- electrophysiologic studies
Algoritmo de tratamiento
hemodynamically unstable
hemodynamically stable
recurrent atrial flutter or failure of elective cardioversion
Colaboradores
Autores
Katherine C. Wu, MD, FACC
Associate Professor of Medicine
Johns Hopkins University
School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Divulgaciones
KCW declares that she has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Richard C. Wu, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Director
Cardiac Electrophysiology Laboratory
UT Southwestern Medical Center
University Hospital
St. Paul
Dallas
TX
Divulgaciones
RCW declares that he has no competing interests.
Reginald Ho, MD
Clinical Assistant Professor
Department of Medicine
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
RH declares that he has no competing interests.
George Juang, MD, FACC
Director of Electrophysiology
Long Island Arrhythmia Center
Mineola
NY
Disclosures
GJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Page RL, Joglar JA, Caldwell MA, et al. 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Apr 5;67(13):e27-115.Full text Abstract
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): the Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):373-498.Full text Abstract
Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation. 2024 Jan 2;149(1):e1-156.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
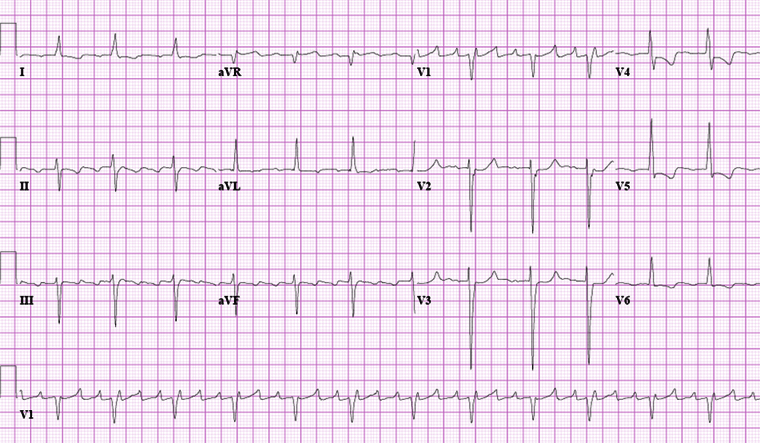
Differentials
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial tachycardia
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on clinical practice guidelines
- 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation
More GuidelinesPatient information
Atrial fibrillation: what is it?
Atrial fibrillation: what are the treatment options?
More Patient information医学计算器
Atrial Fibrillation CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc Score for Stroke Risk
HAS-BLED Bleeding Risk Score
更多 医学计算器Videos
Electrical (direct current) cardioversion animated demonstration
更多 操作视频登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明