Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- nonspecific pain at site of infection
- back pain
- malaise and fatigue
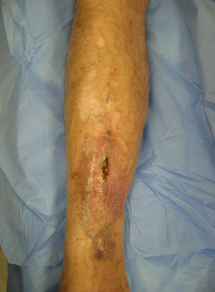
- local inflammation, erythema, or swelling
- low-grade fever
Other diagnostic factors
- sinus and/or wound drainage
- reduced range of movement
- reduced sensation
- urinary tract symptoms
- torticollis
- limb deformity
- tenderness to percussion
Risk factors
- previous osteomyelitis
- penetrating injuries
- surgical contamination
- distant or local infections
- intravenous drug misuse
- diabetes mellitus
- immunocompromise
- sickle cell anemia
- upper respiratory tract infection
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- WBC count
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CRP
- plain x-rays of affected area
- blood culture
- MRI of bone
- guided bone biopsy or open bone biopsy
Tests to consider
- ultrasound
- CT scan
- radionuclide scans
- three-phase bone scans
- histology
- procalcitonin
Treatment algorithm
suspected acute peripheral osteomyelitis
suspected acute osteomyelitis in diabetic foot
suspected acute native vertebral osteomyelitis
confirmed acute peripheral osteomyelitis: adults and children
confirmed acute osteomyelitis in diabetic foot: adults and children
confirmed acute native vertebral osteomyelitis: adults and children
chronic osteomyelitis
Contributors
Expert advisers
Tessa Gomez, MD
Attending, Department of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases, Mount Sinai Beth Israel
Associate Professor, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York
NY
Disclosures
TG declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Tessa Gomez would like to gratefully acknowledge Mr Adrian Kendal, Dr Jamie Ferguson, Dr Tse Hua Nicholas Wong, Dr Bridget L. Atkins, Dr Martin McNally, Dr Jason H. Calhoun, Dr Nalini Rao, and Dr M.M. Manring, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
JF received a research grant in 2013 from Bonesupport AB, Lund, Sweden to collect data for a study on antibiotic carriers in osteomyelitis treatment. JF is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. BLA is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. MM is an executive board member of the European Bone & Joint Infection Society and the Girdlestone Orthopaedic Society. He has performed consultancy work for Bonesupport AB and the Oxford Bone Infection Consultancy. He has received travel expenses from Bonesupport AB and the AO Foundation to attend scientific conferences and symposia. He has received royalties from Oxford University Press for contributions to textbooks. MM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. AK, THNW, JHC, NR, and MMM declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Kristine Johnson, MD
Assistant Professor
Infectious Diseases
Bayview Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
KJ declares that she has no competing interests.
Silvano Esposito, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Infectious Diseases
University of Naples
Naples
Italy
Disclosures
SE has been reimbursed for attending several conferences and received fees for speaking and running educational programs by Pfizer, Novartis, Wyeth Lederle, Sanofi Aventis, and GSK.
Edward Pesanti, MD
Professor of Medicine
Infectious Diseases Division
University of Connecticut Health Center
Hartford
CT
Disclosures
EP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Woods CR, Bradley JS, Chatterjee A, et al. Clinical practice guideline by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America: 2021 guideline on diagnosis and management of acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in pediatrics. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2021 Sep 23;10(8):801-44.Full text Abstract
Berbari EF, Kanj SS, Kowalski TJ, et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Sep 15;61(6):e26-46.Full text Abstract
Senneville É, Albalawi Z, van Asten SA, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 2:ciad527.Full text Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, or soft tissue infection (excluding spine and diabetic foot). 2022 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Septic arthritis
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Transient synovitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR appropriateness criteria: suspected osteomyelitis of the foot in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Guide to utilization of the microbiology laboratory for diagnosis of infectious diseases: 2024 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society for Microbiology (ASM)
More GuidelinesPatient information
Osteomyelitis
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer