Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- polyuria
- polydipsia
- diabetic ketoacidosis
Other diagnostic factors
- young age
- weight loss
- blurred vision
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
- tachypnea
- clinical dehydration
- lethargy
- altered mental status
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition
- geographic region
- infectious agents
- dietary factors
- use of immunotherapy
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- HbA1c
- fasting plasma glucose
- 2-hour post-glucose load plasma glucose
- random plasma glucose
Tests to consider
- plasma or urine ketones
- random C-peptide
- autoimmune markers
Treatment algorithm
nonpregnant
pregnant
Contributors
Authors
Rajesh K. Garg, MD

Professor of Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Harbor-UCLA Medical Center
Torrance
CA
Disclosures
RKG is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Rajesh K. Garg would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Varsha Vimalananda, previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
VV declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Zachary Bloomgarden, MD
Clinical Professor
Medicine/Endocrinology
Diabetes and Bone Disease
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
New York
NY
Disclosures
ZB declares that he has no competing interests.
Alicia Jenkins, MB, BS, MD, FRACP, FRCP
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
University of Melbourne
Melbourne
Australia
Professor
Harold Hamm Oklahoma Diabetes Center
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Oklahoma City
OK
Disclosures
AJ has been a (non-salaried) co-investigator on multi-center clinical trials supported by Novo, Eli Lilly, Sanofi-Aventis, and Medtronic. She does not hold any stocks or shares in these companies. She has received a speaker's honorarium from Novo Nordisk.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
American Diabetes Association. Standards of care in diabetes - 2025. Diabetes Care. 2025 Jan;48(1):S344-52.Full text
Norris JM, Johnson RK, Stene LC. Type 1 diabetes-early life origins and changing epidemiology. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Mar;8(3):226-38.Full text Abstract
International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2024. Dec 2024 [nternet publication].Full text
Holt RIG, DeVries JH, Hess-Fischl A, et al. The management of type 1 diabetes in adults. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2021 Dec;64(12):2609-52.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
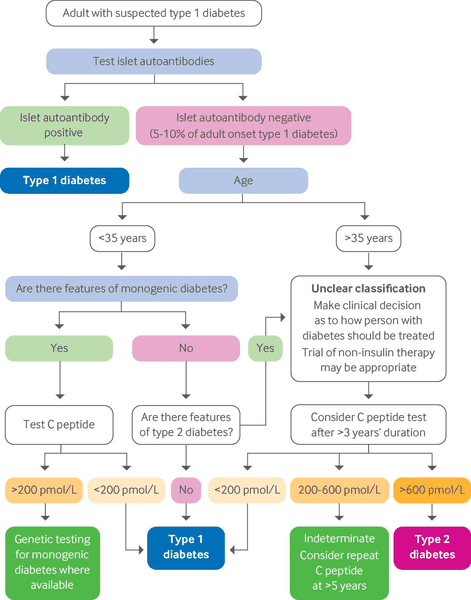
Differentials
- Monogenic diabetes: maturity onset diabetes of the young
- Monogenic diabetes: neonatal diabetes mellitus
- Type 2 diabetes
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Standards of care in diabetes - 2025
- Management of individuals with diabetes at high risk for hypoglycemia
More GuidelinesPatient information
Diabetes type 1: what is it?
Diabetes type 1: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer