WHO recommends first single-dose drug for Plasmodium vivax malaria
The World Health Organization (WHO) have included tafenoquine as a treatment option in the latest update of their guidelines for malaria. Tafenoquine is an 8-aminoquinoline antimalarial drug with activity against all stages of the P vivax life cycle.
WHO recommends tafenoquine as an alternative to primaquine for preventing relapses of P vivax malaria in patients ages ≥2 years who have ≥70% glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity and who are receiving treatment with chloroquine. It is recommended in South America only.
This marks a major milestone in advancing access to a single-dose drug for achieving radical cure (treatment of both the blood- and liver-stages of the disease) in endemic countries, and provides an opportunity to overcome the challenges associated with adherence to the existing 7- or 14-day primaquine treatment regimens.
Tafenoquine has the potential to cause hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency. Therefore, appropriate G6PD testing must be performed before prescribing the drug. It has been associated with psychiatric adverse effects and should not be used in people with a history of a psychotic disorder. Other common adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, and insomnia. Antirelapse treatment with either primaquine or tafenoquine is contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding.[49][104]
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) currently recommends tafenoquine for antirelapse treatment in patients with either P vivax or P ovale malaria, and only recommends use in adolescents ages ≥16 years and nonpregnant adults.[104]
The updated WHO guideline also contains new recommendations for malaria vaccines and the use of near-patients qualitative and semiquantitative G6PD tests to guide antirelapse treatment of P vivax and P ovale infection.
According to the latest report, there were an estimated 263 million malaria cases and 597,000 deaths globally in 2023.[7] P vivax is the dominant malaria parasite in most countries outside of sub-Saharan Africa.
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- fever or history of fever
Other diagnostic factors
- headache
- weakness
- myalgia
- arthralgia
- anorexia
- diarrhea
- seizures
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
- pallor
- hepatosplenomegaly
- jaundice
- altered level of consciousness
- hypotension
- bleeding
- anuria/oliguria
- tachypnea
Risk factors
- travel to endemic area
- inadequate or absent chemoprophylaxis
- insecticide-treated bed net not used in endemic area
- low host immunity (severe disease)
- pregnancy (severe disease)
- age <5 years (severe disease)
- immunocompromise (severe disease)
- older age (severe disease)
- malnutrition (severe disease)
- iron administration (children)
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
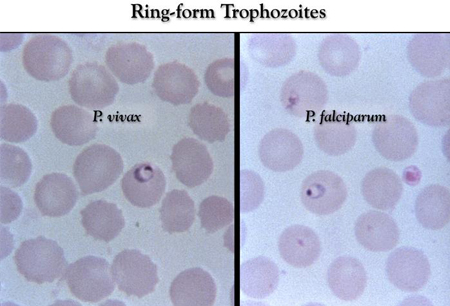
- Giemsa-stained thick and thin blood smears
- rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs)
- CBC
- clotting profile
- serum electrolytes, BUN and creatinine
- serum LFTs
- serum blood glucose
- urinalysis
- arterial blood gas
Tests to consider
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) blood for malaria
- chest x-ray
- blood culture
- urine culture
- sputum culture
- lumbar puncture
- HIV test
- PCR nasopharyngeal swabs for influenza or COVID-19
- CT head
Emerging tests
- loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Treatment algorithm
severe disease (or unable to take oral medication initially): all Plasmodium species
Plasmodium falciparum (or unknown species): uncomplicated disease
Plasmodium ovale: uncomplicated disease
Plasmodium vivax: uncomplicated disease
Plasmodium malariae or Plasmodium knowlesi: uncomplicated disease
Plasmodium falciparum: recurrent infection
Contributors
Authors
Elizabeth Ashley, MB BS, FRCP, FRCPath
Director
Institution Lao-Oxford-Mahosot Hospital - Wellcome Trust Research Unit
Vientiane
Laos
Honorary Consultant in Infectious Diseases and Microbiology
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Professor of Tropical Medicine
University of Oxford
Oxford
UK
Disclosures
EA is an associate editor of Malaria Journal, an academic editor for PLOS Medicine, and is on the Lancet Infectious Diseases International Advisory Board. EA is on the council of the International Society for Infectious Diseases. The Institution Lao-Oxford-Mahosot Hospital - Wellcome Trust Research Unit receives core funding from the Wellcome Trust. EA is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Arjun Chandna, BA MRCP AFHEA
Clinical Research Fellow
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health
University of Oxford
Oxford
Specialty Registrar in Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology
University College London Hospitals NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
None.
Acknowledgements
Dr Elizabeth Ashley and Dr Arjun Chandna would like to gratefully acknowledge Professor Ron Behrens, Mariyam Mirfenderesky, Dr Signe Maj Sorensen, Dr Joanna Allen, Dr Simon Warren, and Dr Behzad Nadjm, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
RB acted as a paid expert to the courts on malaria prophylaxis. RB received fees on the Travel Health advisory board for Emergent BioSolutions. RB prepared education material for the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow. RB is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. MM, SMS, JA, and SW declare that they have no competing interests. BN is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Blaise Genton, MD
Professor
Head of the Travel Clinic
Consultant of Tropical and Travel Medicine
University Hospital
Project Leader
Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute
Basel
Switzerland
Disclosures
BG has received a research grant from Novartis Pharma to assess the impact of the introduction of artemether-lumefantrine (Novartis) as first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria on mortality of children under 5 years old in 2 districts in Tanzania and travel grants from Novartis Pharma to present the results of the study above. BG is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
David Sullivan, MD
Associate Professor
Malaria Research Institute and Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
DS has received royalties from antigen provision for a diagnostic test to Inverness. DS with Johns Hopkins University has patents on diagnostic tests that do not require blood.
Walther H. Wernsdorfer, MD
Professor
Institute of Specific Prophylaxis and Tropical Medicine
Medical University of Vienna
Vienna
Austria
Disclosures
WHW declares that he has no competing interests.
References
Key articles
World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for malaria. Nov 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical guidance: malaria diagnosis & treatment in the U.S. Jun 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Dengue fever
- Zika virus infection
- Chikungunya virus
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- WHO guidelines for malaria
- Malaria diagnosis and treatment in the US
More GuidelinesPatient information
Malaria prevention
More Patient informationVideos
Diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer