Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- soft-tissue swelling
Other diagnostic factors
- multiple sinuses
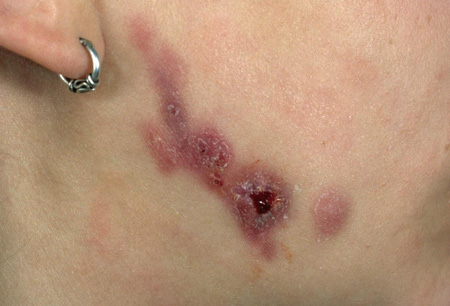
- skin discoloration
- chewing difficulties
- constitutional symptoms
- change in bowel habits
- abdominal discomfort
- nausea and vomiting
- sensation of abdominal mass
- vaginal bleeding or discharge
- dry or productive cough
- blood-streaked sputum
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- focal neurologic defects
Risk factors
- male sex
- injury or inflammation of the oral cavity
- diabetes mellitus
- immunosuppression
- local tissue damage by neoplasia, trauma, or irradiation
- intrauterine device
- aspiration
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- culture of pus or affected tissue
- histology of affected tissue
- immunohistology
- CBC
- CT or MRI of abdomen
Emerging tests
- PCR of affected tissue
Treatment algorithm
non-penicillin allergic
penicillin allergic
Contributors
Authors
Thomas Schneider, MD, PhD
Professor
Medical Department I
Charité - University Medicine Berlin
CBF
Berlin
Germany
Disclosures
TS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Verena Moos, PhD
Scientist
Medical Department I
Charité - University Medicine Berlin
CBF
Berlin
Germany
Disclosures
VM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Johannes R. Bogner, MD
Professor of Internal Medicine
Department of Infectious Diseases
Medical Polyclinic
University Hospital Munich
Munich
Germany
Disclosures
JRB declares that he has no competing interests.
Chris Huston, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases
University of Vermont
Burlington
VT
Disclosures
CH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Smego RA Jr, Foglia G. Actinomycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1998 Jun;26(6):1255-61. Abstract
Acevedo F, Baudrand R, Letelier LM, et al. Actinomycosis: a great pretender: case reports of unusual presentations and a review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2008 Jul;12(4):358-62. Abstract
Wong VK, Turmezei TD, Weston VC. Actinomycosis. BMJ. 2011 Oct 11;343:d6099. Abstract
Martin MV. The use of oral amoxycillin for the treatment of actinomycosis: a clinical and in vitro study. Br Dent J. 1984 Apr 7;156(7):252-4. Abstract
Spilsbury BW, Johnstone FR. The clinical course of actinomycotic infections: a report of 14 cases. Can J Surg. 1962 Jan;5:33-48. Abstract
Sudhakar SS, Ross JJ. Short-term treatment of actinomycosis: two cases and a review. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Feb 1;38(3):444-7.Full text Abstract
Bennhoff DF. Actinomycosis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations and a review of 32 cases. Laryngoscope. 1984 Sep;94(9):1198-217. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Abdominal abscess
- Ovarian or oviductal tumor
- Appendicitis
More DifferentialsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer