Summary
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- positive family history
- presence of an associated syndrome
- decreased peripheral vision
- night blindness
- impaired dark adaptation
- decreased central acuity
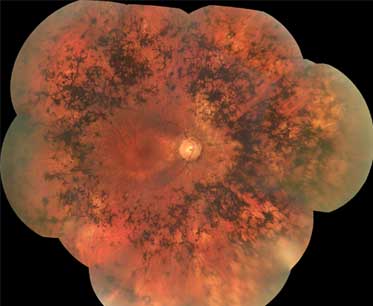
- atrophy of retinal pigment epithelium
- bone spicule pigmentation
Otros factores de diagnóstico
- waxy pale optic nerve
- photopsias
- refractive error
- cataracts
- retinal vascular attenuation
- cystoid macular edema
- vitreous cells
- glare from bright lights
- abnormal color vision
- keratoconus
- glaucoma
- optic nerve head drusen
- Coats-like retinopathy
- Leber congenital amaurosis
Factores de riesgo
- family history
- presence of an associated syndrome
Pruebas diagnósticas
Primeras pruebas diagnósticas para solicitar
- assessment of visual acuity
- anterior segment exam and intraocular pressure measurement
- full field perimetry
- full field electroretinogram (ERG)
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- elevated final dark-adapted threshold
- optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- genetic testing
- adaptive optics imaging
- wide-field fundus autofluorescence (FAF)
Pruebas emergentes
- whole exome sequencing
Algoritmo de tratamiento
all patients
Colaboradores
Autores
Lesley Everett , MD, PhD, MPhil
Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology
Casey Eye Institute
Oregon Health and Sciences University
Divisions of Ophthalmic Genetics and Retina
Portland
OR
Divulgaciones
LAE is supported by a Foundation Fighting Blindness Career Development Grant.
Mark E. Pennesi, MD, PhD

Professor
Casey Eye Institute
Oregon Health and Sciences University
Portland
OR
Divulgaciones
MEP serves on the scientific advisory board and executive committee for the Foundation Fighting Blindness.
Paul Yang, MD, PhD

Associate Professor
Casey Eye Institute
Oregon Health and Sciences University
Portland
OR
Divulgaciones
PY acted as a consultant for 4D Molecular Therapeutics, AAVantgarde Bio (IDMC), Adverum, Astellas, Beacon Therapeutics, BlueRock Therapeutics, Eluminex Biosciences, Foundation Fighting Blindness (SAB), Janssen (DSMB), MieraGTx (DSMB), Nanoscope Therapeutics (SAB), and TeamedOn.
Agradecimientos
Dr Lesley Everett, Dr Mark E. Pennesi, and Dr Paul Yang would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard G. Weleber and Dr Peter J. Francis, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
RGW has served as a consultant to Novartis, Pfizer, and Wellstat, is a member of the scientific advisory board for Applied Genetic Technologies Corp, and serves on the scientific advisory board for the Foundation Fighting Blindness (the relationship has been reviewed and managed by Oregon Health & Science University). RGW also reports having received grants and personal fees from the Foundation Fighting Blindness and Applied Genetic Technologies Corp, and other support from Sanofi-Fovea, all outside the submitted work. In addition, RGW has a patent (US patent 8,657,446, Method and apparatus for visual field monitoring, also known as Visual Field Monitoring and Analysis, or VFMA, which has not been issued). PJF declares that he has no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Scott Fraser, MD, FRCS (Ed), FRCOphth
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Sunderland Eye Infirmary
Sunderland
UK
Divulgaciones
SF declares that he has no competing interests.
Elias Traboulsi, MD
Professor of Ophthalmology
Director
Center for Genetic Eye Diseases
Cole Eye Institute
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland
OH
Divulgaciones
ET declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Comprehensive adult medical eye evaluation PPP. Nov 2020 [internet publication].Texto completo
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Guidelines on clinical assessment of patients with inherited retinal degenerations - 2022. Oct 2022 [internet publication].Texto completo
Robson AG, Frishman LJ, Grigg J, et al. ISCEV Standard for full-field clinical electroretinography (2022 update). Doc Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun;144(3):165-77.Texto completo Resumen
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Recommendations for genetic testing of inherited eye diseases. February 2014 [internet publication].Texto completo
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
Diferenciales
- Congenital rubella
- Syphilis
- Vitamin A deficiency
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- Guidelines on clinical assessment of patients with inherited retinal degenerations
- Pediatric eye evaluations preferred practice pattern
Más Guías de práctica clínicaInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad