Summary
Definition
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- age 10-19 or 30-39 years
- motor weakness
- paresthesias or sensory loss
- bladder symptoms: urinary frequency, urgency, incontinence, or retention
- bowel symptoms: incontinence or constipation
- L'hermitte sign
- McArdle sign
- paroxysmal tonic spasms
- upper motor neuron signs: hyperreflexia, positive Babinski sign, limb spasticity
- sensory loss/sensory level
- dyspnea/respiratory distress
其他诊断因素
- back pain
- trunk/limb pain
- areflexia/hyporeflexia
- hiccups
- nausea/vomiting
危险因素
- preceding infectious illness
- recent vaccination
- female sex
- history of recent physical trauma
- spinal injection
诊断性检查
首要检查
- MRI spinal cord
- MRI brain
- serum aquaporin-4 autoantibodies and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein autoantibodies
- cerebrospinal fluid cell count, cell differential, protein level, IgG index, oligoclonal bands
- cerebrospinal fluid Gram stain, cultures (bacterial, tubercular, fungal), and India ink smear
- cerebrospinal fluid, polymerase chain reaction for herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1, HSV-2, varicella zoster virus (VZV), Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease), cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and West Nile virus
- cerebrospinal fluid Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test
- serum anti-nuclear antibody, double-stranded DNA
- extractable nuclear antigen (including SSA and SSB autoantibodies)
- serum and cerebrospinal fluid paraneoplastic autoantibodies
- other neural autoantibodies
需考虑的检查
- serum and cerebrospinal fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme
- CXR
- CT body (chest, abdomen, and pelvis)
- whole-body PET scan
- cerebrospinal fluid cytology and flow cytometry
- serology for herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1, HSV-2, varicella zoster virus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, and West Nile virus
- urinalysis
- HIV antibodies
- visual-evoked potential
- optical coherence tomography
- therapeutic trial with corticosteroid
- spinal cord biopsy
治疗流程
acute neurologic deficits
idiopathic transverse myelitis (TM)
at risk for multiple sclerosis (MS) (typical demyelinating lesions on MRI)
aquaporin-4 (AQP4) autoantibody seropositive
myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-IgG autoantibody seropositive
撰稿人
作者
Cristina Valencia-Sanchez, MD, PhD
Department of Neurology
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale
AZ
利益声明
CVS declares that she has served on an advisory board for TG Therapeutics.
鸣谢
Dr Cristina Valencia-Sanchez would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Dean Wingerchuk, the previous contributor to this topic. DMW has received compensation from MedImmune for service on a clinical trial adjudication committee, from Caladrius for consulting services, and research support paid to Mayo Clinic from Alexion and TerumoBCT. DMW is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
同行评议者
Alireza Minagar, MD
Assistant Professor of Neurology
LSU Health Sciences Center
Shreveport
LA
利益声明
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
Cory Toth, BSc, MD, FRCP(C)
Assistant Professor of Neurosciences
Hotchkiss Brain Institute
University of Calgary
Alberta
Canada
利益声明
CT declares that he has no competing interests.
Abhijit Chaudhuri, DM, MD, PhD, FACP, FRCP
Consultant Neurologist
Clinical Director of Neurosciences
Department of Neurology
Queen's Hospital
Romford
UK
利益声明
AC declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
参考文献
关键文献
Transverse Myelitis Consortium Working Group. Proposed diagnostic criteria and nosology of acute transverse myelitis. Neurology. 2002 Aug 27;59(4):499-505. 摘要
Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging, Agarwal V, Shah LM, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® myelopathy: 2021 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 May;18(5s):S73-82.全文 摘要
Rae-Grant A, Day GS, Marrie RA, et al. Practice guideline recommendations summary: disease-modifying therapies for adults with multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2018 Apr 24;90(17):777-88.全文 摘要
参考文献
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
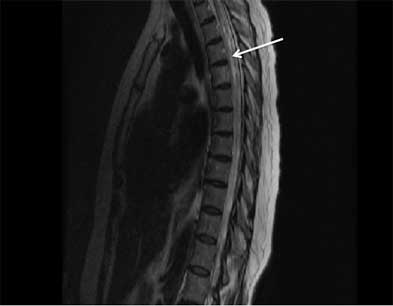
鉴别诊断
- Compressive myelopathy
- Infectious myelitis (e.g., tuberculosis)
- Anterior spinal artery occlusion
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- ACR appropriateness criteria: myelopathy
- Practice guideline: disease modifying therapies in adults with multiple sclerosis
更多 指南患者教育信息
Multiple sclerosis
更多 患者教育信息登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明