Summary
Definition
History and exam
Other diagnostic factors
- constitutional symptoms
- pyrexia
- jaundice
- hepatosplenomegaly
- petechiae, splinter hemorrhages, or ecchymoses
- dark urine
- conjunctival injection
- cough
- sore throat
- photophobia
Risk factors
- residence in or travel to an endemic region
- exposure to Ixodes scapularis ticks
- blood transfusion
- asplenia
- immunosuppression
- age >50 years
- Lyme disease
- human granulocytic anaplasmosis
- maternal infection during pregnancy
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
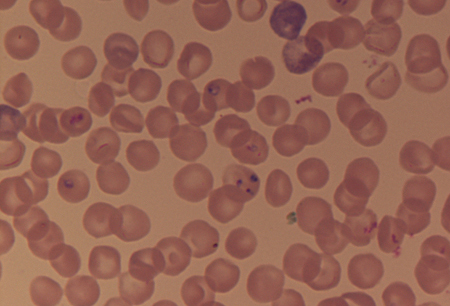
- peripheral blood smear (Giemsa or Wright stained)
- polymerase chain reaction for babesial DNA
- CBC
- LFTs
- serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- urinalysis
- ELISA and/or immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease
- polymerase chain reaction and/or immunofluorescence assay or buffy coat smear for human granulocytic anaplasmosis
Investigations to consider
- indirect immunofluorescence antibody assay for Babesia microti
- IgG/IgM immunoblot for Lyme disease
- HIV serology
Treatment algorithm
asymptomatic documented infection
mild to moderate disease
acute severe disease
recurrent or refractory disease
Contributors
Authors
Sarah Hochman, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases and Immunology
New York University School of Medicine
New York
NY
Disclosures
SH declares that she has no competing interests.
Louis Weiss, MD, MPH

Professor of Medicine
Division of Infectious Diseases
Professor of Pathology
Division of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Bronx
NY
Disclosures
LW has received grant funding from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. He is also the author of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Jeremy Gray, BSc, MSc, PhD
Professor
Department of Environmental Resource Management
University College Dublin
Belfield
Dublin
Republic of Ireland
Disclosures
JG declares that he has no competing interests.
Sam Telford III, ScD
Associate Professor of Biomedical Sciences
Division of Infectious Diseases
Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine
Tufts University
Boston
MA
Disclosures
ST has active research funding from the NIH. ST is an author or co-author of numerous primary publications on the biology of babesiosis, as well as reviews that have been referenced in this topic.
Raymond J. Dattwyler, MD
Professor of Medicine and Microbiology/Immunology
Chief of Allergy, Immunology and Rheumatology
New York Medical College
Valhalla
NY
Disclosures
RJD declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Vannier E, Krause PJ. Human babesiosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2397-2407. Abstract
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Tickborne diseases of the United States: a reference manual for health care providers, sixth edition. Aug 2022 [internet publication].Full text
Krause PJ, Auwaerter PG, Bannuru RR, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA): 2020 guideline on diagnosis and management of Babesiosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jan 27;72(2):e49-e64.Full text Abstract
Sanchez E, Vannier E, Wormser GP, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of Lyme disease, human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and babesiosis: a review. JAMA. 2016;315:1767-77. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Lyme disease
- Human granulocytic anaplasmosis
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Tickborne diseases of the United States: a reference manual for health care providers
- 2020 Guideline on diagnosis and management of babesiosis
More GuidelinesPatient information
Lyme disease
Malaria prevention
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer