Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- age <3 years
- leukocoria (white pupillary reflex)
- strabismus
- positive family history
- orbital pseudocellulitis
- 13q syndrome
Other diagnostic factors
- visual disturbances
- ocular pain
- pinealoma
Risk factors
- mutation in RB1 gene
- human papillomavirus (HPV) exposure
- advanced paternal age
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- funduscopy and examination under anesthesia
- wide-field fundus photography and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (sdOCT)
- ophthalmic A- and B-scan ultrasound
Investigations to consider
- genetic testing
- MRI head/orbit
- bone marrow aspiration
- lumbar puncture
Emerging tests
- liquid biopsy
Treatment algorithm
with vitreous seeding
without vitreous seeding
metastatic disease
recurrence
Contributors
Authors
Timothy G. Murray, MD, MBA, FACS
Founding Director/CEO
Murray Ocular Oncology and Retina
Miami
FL
Disclosures
TGM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Victor M. Villegas, MD
Ocular Oncologist
Associate Professor
Department of Ophthalmology
University of Puerto Rico
Associate Professor
Department of Surgery
Ponce Health Sciences University School of Medicine
Voluntary Faculty
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute
University of Miami
Miami
FL
Disclosures
VMV is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Timothy G. Murray and Dr Victor M. Villegas would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Amy C. Schefler, a previous contributor to this topic, and Dr Steven Houston, III, MD for his contribution to the topic.
Disclosures
ACS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic. SH declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Susan Schneider, MD
Director
Pharmaceutical Clinical & Scientific Affairs
Bausch & Lomb
Rochester
NY
Disclosures
SS declares that she has no competing interests.
Francis Munier, MD
Professor and Head of Pediatric Ocular Oncology Unit
Jules Gonin Eye Hospital
Lausanne
Switzerland
Disclosures
FM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Kamihara J, Bourdeaut F, Foulkes WD, et al. Retinoblastoma and neuroblastoma predisposition and surveillance. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jul 1;23(13):e98-106.Full text Abstract
Global Retinoblastoma Study Group. The Global Retinoblastoma Outcome Study: a prospective, cluster-based analysis of 4064 patients from 149 countries. Lancet Glob Health. 2022 Aug;10(8):e1128-40.Full text Abstract
Skalet AH, Gombos DS, Gallie BL, et al. Screening children at risk for retinoblastoma: consensus report from the American Association of Ophthalmic Oncologists and Pathologists. Ophthalmology. 2018 Mar;125(3):453-8.Full text Abstract
de Graaf P, Goricke S, Rodjan F, et al. Guidelines for imaging retinoblastoma: imaging principles and MRI standardization. Pediatr Radiol. 2012 Jan;42(1):2-14.Full text Abstract
American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria: orbits, vision and visual loss. 2017 [internet publication].Full text Abstract
Hutchinson AK, Morse CL, Hercinovic A, et al. Pediatric eye evaluations preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2023 Mar;130(3):P222-70.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
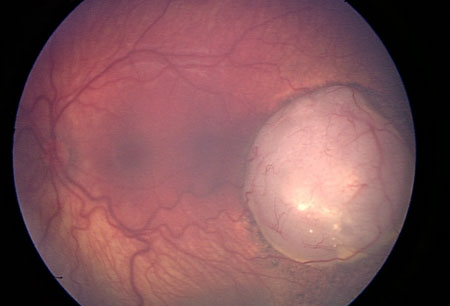
Differentials
- Coats disease (exudative retinitis or retinal telangiectasis)
- Persistent fetal vasculature (formerly known as persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous)
- Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Pediatric eye evaluations preferred practice pattern
- Screening children at risk for retinoblastoma
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer