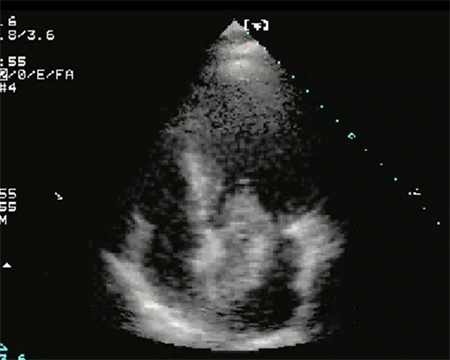
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- dyspnea
- syncope
- dizziness
- CHF/pulmonary edema
- embolic manifestations
- systolic or diastolic murmur
- tumor plop
Other diagnostic factors
- weight loss
- fatigue
- fever
- pallor
- arthralgia
- Raynaud phenomenon
- loud first heart sound
- opening snap
- Carney complex
- intracerebral aneurysm
Risk factors
- family history of atrial myxoma
- female sex
- age 40-60 years
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- echocardiogram
- ECG
- CBC
- CXR
Tests to consider
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- C-reactive protein
- protein electrophoresis
- CT scan (chest)
- MRI scan (chest)
- biopsy
Treatment algorithm
surgical candidate
non-surgical candidate
Contributors
Authors
Syed Wamique Yusuf, MBBS, FRCPI

Professor of Medicine
Department of Cardiology
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
SWY declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Syed Wamique Yusuf would like to gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Dr Daniel J. Lenihan.
Disclosures
DJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Paul Heidenreich, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Stanford University
Stanford
CA
Disclosures
PH declares that he has no competing interests.
Richard Steingart, MD
Chief
Cardiology Service
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
New York
NY
Disclosures
RS declares that he has no competing interests.
Barry Kneale, MD, FRCP
Integrated Lead Cardiologist
Western Sussex Hospitals NHS Trust and Cardiac Department
Worthing Hospital
Worthing
UK
Disclosures
BK declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Pinede L, Duhaut P, Loire R. Clinical presentation of left atrial cardiac myxoma. A series of 112 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2001 May;80(3):159-72. Abstract
Edwards A, Bermudez C, Piwonka G, et al. Carney's syndrome: complex myxomas. Report of four cases and review of the literature. Cardiovasc Surg. 2002 Jun;10(3):264-75. Abstract
Grossniklaus HE. McLean IW, Gillespie JJ. Bilateral eyelid myxomas in Carney's complex. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991 Apr;75(4):251-2.Full text Abstract
Ohara N, Komiya I, Yamauchi K, et al. Carney's complex with primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease and spotty pigmentations. Intern Med. 1993 Jan;32(1):60-2.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
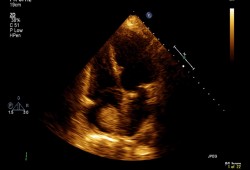
Differentials
- Mitral stenosis
- Infective endocarditis
- Atrial thrombus
More DifferentialsLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer