Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- newborn and toddler age
- abnormal location of urethra
- incomplete prepuce
- penile curvature and/or torsion
- recent genital exam or procedure
- history of short or small penis
- penile pain and swelling
- foreskin adherent to glans
- penile adhesions and smegma
- penile cicatrix
- penile glans edema
- prominent prepubic fat pad
- presence of hernia or hydrocele
Other diagnostic factors
- forced retraction of foreskin
- dyspareunia
- recent penile trauma
- history of balanitis or balanoposthitis
- urinary obstruction or retention
- necrosis of penile skin
- discoloration of glans
- penile length discrepancy
- history of urinary tract infection
- history of pelvic or genitourinary surgery
- erectile dysfunction
Risk factors
- uncircumcised penis (paraphimosis)
- indwelling urinary catheter (paraphimosis)
- parental unawareness (phimosis)
- balanitis xerotica obliterans (phimosis)
- penile trauma (phimosis)
- recurrent balanitis and balanoposthitis (phimosis)
- low birth weight (hypospadias)
- preterm delivery (hypospadias)
- gestational diabetes, maternal obesity, maternal hypertension, older maternal age (hypospadias)
- family history (hypospadias, congenital penile curvature and/or torsion)
- obesity (buried penis)
- circumcision (trapped penis)
- penile and lower abdominal scarring (buried penis)
- hernia or hydrocele (buried penis)
- SRD5A2 gene V89L polymorphism (hypospadias)
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- clinical diagnosis
Treatment algorithm
prepubertal phimosis, congenital or physiologic
postpubertal phimosis
paraphimosis
hypospadias
congenital penile curvature and/or torsion
concealed penis <3 years old (before toilet training)
concealed penis ≥3 years old (after toilet training)
micropenis
Contributors
Authors
Kathleen Kieran, MD, MSc, MME
Director of Pediatric Urology Fellowship
Professor and Vice Chair for Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
Department of Urology
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
KK declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Kathleen Kieran would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Nicol Corbin Bush, Dr Nicholas Cost, Dr Linda Baker, and Dr Michael Holzer, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
NCB, NC, LB, and MH declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
David Bloom, MD
Chair
Department of Urology
The Jack Lapides Professor of Urology
University of Michigan Medical School
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
DB declares that he has no competing interests.
Vincent Gnanapragasam, MBBS, BMedSci, PhD, FRCSEng, FRCSEd(Urol)
Lecturer in Uro-oncology and Consultant Urological Surgeon
Department of Urology
Addenbrooke's Hospital
Cambridge
UK
Disclosures
VG declares that he has no competing interests.
Laurence Baskin, MD
Chief
Pediatric Urology
and Professor
Urology and Pediatrics
UCSF Children's Hospital
San Francisco
CA
Disclosures
LB declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
European Association of Urology; European Society for Paediatric Urology. EAU guidelines on paediatric urology. Apr 2024 [internet publication].Full text
Dave S, Afshar K, Braga LH, et al. Canadian Urological Association guideline on the care of the normal foreskin and neonatal circumcision in Canadian infants (full version). Can Urol Assoc J. 2018 Feb; 12(2):E76-99.Full text Abstract
British Association of Paediatric Surgeons. Management of foreskin conditions. Jun 2006 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
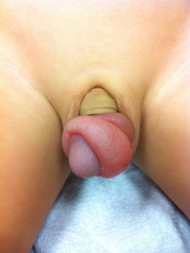
Differentials
- Balanoposthitis
- Encircling foreign body
- Trapped penis
Mais DifferentialsGuidelines
- EAU guidelines on paediatric urology
- Penile circumcision
Mais GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer