Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- age >50 years
- male sex
- geographic location: central Africa or the Mediterranean
- HIV infection
- human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8, also known as Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus [KSHV]) infection
- immunosuppression
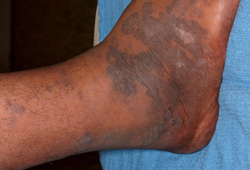
- skin lesion
- oral lesion
- lymphadenopathy
- lymphedema
Other diagnostic factors
- weight loss
- abdominal pain
- gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
- diarrhea
- dyspnea
- hemoptysis
- chest pain
- fever
Risk factors
- male sex
- HIV infection
- immunosuppressive therapy
- human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8, also known as Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus [KSHV]) infection
- central African ethnicity
- drug abuse
- Jewish ethnicity
- Mediterranean ethnicity
- age <5 years or >50 years
- men who have sex with men
- Black American ethnicity
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- HIV test
- CBC and comprehensive metabolic panel
- skin/mucosal biopsy
Tests to consider
- chest x-ray
- chest CT and bronchoscopy
- CT abdomen/pelvis
- MRI
- fecal occult blood
- gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy
- PET scan
- lymph node biopsy
- renal function tests
- liver function tests
Emerging tests
- human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) viremia and serology
Treatment algorithm
HIV-associated KS
classic (sporadic) KS
iatrogenic (transplant-related) KS
endemic (observed in sub-Saharan Africa) KS
Contributors
Authors
David Aboulafia, MD
Attending Hematologist and Oncologist
Virginia Mason Clinical Professor of Medicine
Division of Hematology and Oncology
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
DA is the author of articles cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr David Aboulafia would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Liron Pantanowitz and Dr Bruce J. Dezube, previous contributors to this topic.
Peer reviewers
Justin Stebbing, MA, MRCP, MRCPath, PhD
Consultant Medical Oncologist/Senior Lecturer
Department of Medical Oncology
Imperial College/Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust
Charing Cross Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
JS declares that he has no competing interests.
Thierry Simonart, MD, PhD
Physician
Department of Dermatology
Erasme University Hospital
Brussels
Belgium
Disclosures
TS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: Kaposi sarcoma [internet publication].Full text
Lebbe C, Garbe C, Stratigos AJ, et al; European Dermatology Forum (EDF), the European Association of Dermato-Oncology (EADO), and the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Diagnosis and treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma: European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline (EDF/EADO/EORTC). Eur J Cancer. 2019 Jun;114:117-27. Abstract
National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Panel on Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in Adults and Adolescents with HIV. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in adults and adolescents with HIV. 2025 [internet publication].Full text
National Institutes of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. US Department of Health and Human Services Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents with HIV. 2025 [internet publication].Full text
World Health Organization. Guidelines on the treatment of skin and oral HIV-associated conditions in children and adults. Jan 2014 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Bacillary angiomatosis
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Dermatofibroma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents with HIV
- Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in adults and adolescents with HIV
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer