შეჯამება
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of cardiovascular risk factors
- presence of noncardiovascular risk factors
- palpitations
- tachycardia
- irregular pulse
Other diagnostic factors
- stroke
- shortness of breath
- fatigue
- chest pain
- dizziness
- syncope
- hypotension
- elevated jugular venous pressure
- murmur or gallop rhythm
- rales
- decrease in mentation or listlessness
Risk factors
- hypertension
- coronary artery disease (CAD)
- congestive heart failure
- advancing age
- diabetes mellitus
- valvular disease
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- alcohol misuse
- presence of other arrhythmias
- smoking
- obesity
- sleep-disordered breathing (SDB)
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- sedentary lifestyle
- thyroid disease
- autonomic neuronal dysfunction
- caffeine misuse
- cancer
- working long hours
- excessive exercise
- height
- air pollution
- migraine
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- ECG
- thyroid profile
- echocardiogram
- serum electrolytes (including serum magnesium) and BUN
Tests to consider
- serum aminotransferases
- prolonged ECG monitoring
- fasting blood glucose or HbA1c
- screening for sleep-disordered breathing (SDB)
Treatment algorithm
paroxysmal or persistent AF: hemodynamically unstable
paroxysmal or persistent AF and hemodynamically stable: rate-control strategy selected
paroxysmal or persistent AF and hemodynamically stable: rhythm-control strategy selected
permanent AF
Contributors
Authors
Arti N. Shah, MS, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
New York
NY
Disclosures
ANS declares that she has no competing interests.
Bharat K. Kantharia, MD, FRCP, FAHA, FACC, FESC, FHRS
President, Cardiovascular and Heart Rhythm Consultants
Clinical Professor of Medicine
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Attending and Consultant Cardiac Electrophysiologist
Mount Sinai and New York Presbyterian Hospitals
New York
NY
Disclosures
BKK declares that he has no competing interests. BKK is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Andrew R.J. Mitchell, BM, MD, FRCP, FESC, FACC
Consultant Cardiologist
Jersey General Hospital
St Helier
Jersey
Channel Islands
Disclosures
ARJM declares that he has no competing interests.
Diwakar Jain, MD, FACC, FRCP, FASNC
Professor of Medicine (Cardiology)
Westchester Medical Center
Valhalla
NY
Disclosures
DJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Konstadinos Plestis, MD, FACS
Associate Professor
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery
Mount Sinai Medical Center
New York
NY
Disclosures
KP declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, et al. 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 1;42(5):373-498.Full text
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Atrial fibrillation: diagnosis and management. Jun 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Sharma M, Cornelius VR, Patel JP, et al. Efficacy and harms of direct oral anticoagulants in the elderly for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation and secondary prevention of venous thromboembolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2015 Jul 21;132(3):194-204.Full text Abstract
Lip GY, Haguenoer K, Saint-Etienne C, et al. Relationship of the SAMe-TT₂R₂ score to poor-quality anticoagulation, stroke, clinically relevant bleeding, and mortality in patients with atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2014 Sep;146(3):719-26. Abstract
Kuck KH, Brugada J, Furnkranz A, et al; FIRE AND ICE Investigators. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jun 9;374(23):2235-45.Full text Abstract
Luik A, Radzewtiz A, Kieser M, et al. Cryoballoon versus open irrigated radiofrequency ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the prospective, randomized, controlled, noninferiority FreezeAF Study. Circulation. 2015 Oct 6;132(14):1311-9.Full text Abstract
Del-Carpio Munoz F, Gharacholou SM, Munger TM, et al. Meta-analysis of renal function on the safety and efficacy of novel oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2016 Jan 1;117(1):69-75. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
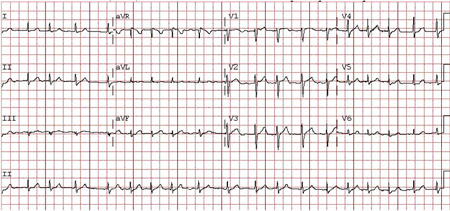
Differentials
- Atrial flutter with variable atrioventricular (AV) conduction
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia with variable AV conduction
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2024 European Heart Rhythm Association/Heart Rhythm Society/Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society/Latin American Heart Rhythm Society expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation
- ACR appropriateness criteria: preprocedural planning for left atrial procedures in atrial fibrillation
More GuidelinesPatient information
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation: what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationCalculators
Atrial Fibrillation CHA(2)DS(2)-VASc Score for Stroke Risk
ORBIT Bleeding Risk Score
More CalculatorsVideos
How to perform an ECG: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer