Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- colicky abdominal pain
- abdominal distention
- nausea
- vomiting
- change in bowel habits
- hard feces
- soft stools
- empty rectum
- recent weight loss
- rectal bleeding
- palpable rectal mass
- palpable abdominal mass
- tympanic abdomen
- abnormal bowel sounds
- fever
- abdominal tenderness
- abdominal rigidity
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- tenesmus
Fatores de risco
- colorectal cancer
- current or previous malignancy
- diverticular disease
- colonic volvulus
- inflammatory bowel disease
- current or previous hernia
- endometriosis
- diabetes
- previous abdominal surgery
- megacolon
- low or high dietary fiber
- laxative abuse
- previous radiation therapy
- ingestion of foreign body
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- CT abdomen and pelvis
- CBC
- serum electrolytes
- CRP
- renal function
- glucose
- coagulation studies, type and screen, cross-match
- blood gas analysis (including lactate)
- serum amylase/lipase
- plain abdominal x-ray
Investigações a serem consideradas
- beta-human chorionic gonadotrophin
- urinalysis
- abdominal ultrasound
- contrast enema
- flexible/rigid endoscopy
- biopsy
Algoritmo de tratamento
acutely ill
sigmoid volvulus
cecal volvulus
colorectal malignancy
diverticular disease
foreign body ingestion
benign strictures
pelvic abscess
currently receiving palliative care
Colaboradores
Consultores especialistas
Adrian A. Maung, MD, MBA, FACS, FCCM
Associate Professor of Surgery
Division of General Surgery, Trauma and Surgical Critical Care
Department of Surgery
Yale School of Medicine
Surgical Director of Perioperative Services
Adult Trauma Medical Director
Yale New Haven Hospital
New Haven
CT
Declarações
AAM declares that he has no competing interests.
Agradecimentos
Dr Adrian A. Maung would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr George Malietzis, Dr John T. Jenkins, and Dr Alisdair J. MacDonald, previous contributors to this topic.
Declarações
GM, JTJ, and AJM declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores
Alessandro Fichera, MD, FACS, FASCRS
Assistant Professor
Department of Surgery
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Declarações
AF declares that he has no competing interests.
Robert H. Diament, MD
Consultant Surgeon
Crosshouse Hospital
Crosshouse
Kilmarnock
UK
Declarações
RHD declares that he has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Alavi K, Poylin V, Davids JS, et al. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons clinical practice guidelines for the management of colonic volvulus and acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. Dis Colon Rectum. 2021 Sep 1;64(9):1046-57.Texto completo Resumo
Pisano M, Zorcolo L, Merli C, et al. 2017 WSES guidelines on colon and rectal cancer emergencies: obstruction and perforation. World J Emerg Surg. 2018 Aug 13;13:36.Texto completo Resumo
Naveed M, Jamil LH, Fujii-Lau LL, et al. American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy guideline on the role of endoscopy in the management of acute colonic pseudo-obstruction and colonic volvulus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Feb;91(2):228-35. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
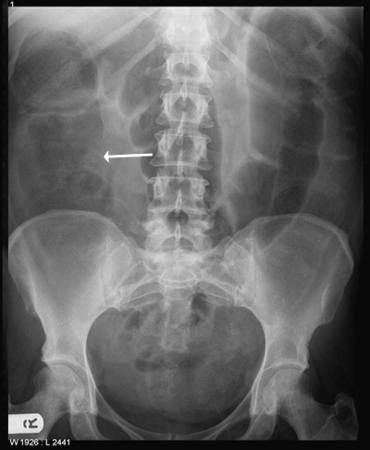
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction (Ogilvie syndrome)
- Chronic/idiopathic megacolon
- Toxic megacolon
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- WSES consensus guidelines on sigmoid volvulus management
- 2017 WSES guidelines on colon and rectal cancer emergencies: obstruction and perforation
Mais DiretrizesVideos
Venepuncture and phlebotomy: animated demonstration
Central venous catheter insertion: animated demonstration
Mais vídeosFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Bowel cancer
Bowel cancer: questions to ask your doctor
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal