Imagens e vídeos
IMAGENS
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
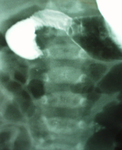
Upper GI contrast study demonstrating malrotation with volvulus. The duodenum fails to develop the normal anatomical C-loop. There is failure of contrast to pass, resulting in a characteristic bird beak consistent with acute mid-gut volvulus
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
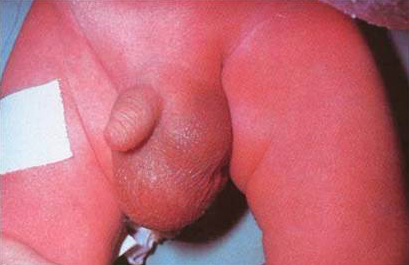
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
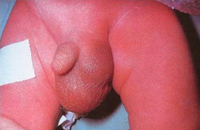
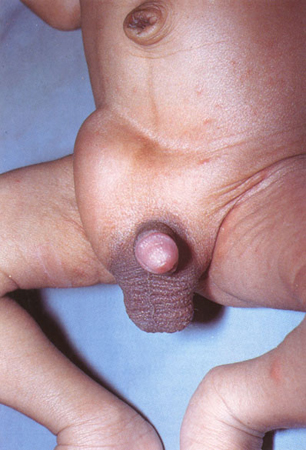
Infant with right groin bulge consistent with incarcerated inguinal hernia. The lack of overlying skin oedema and erythema does not rule out strangulation of the small intestine
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
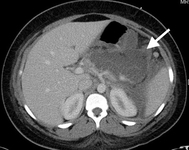
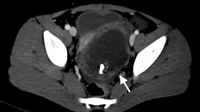
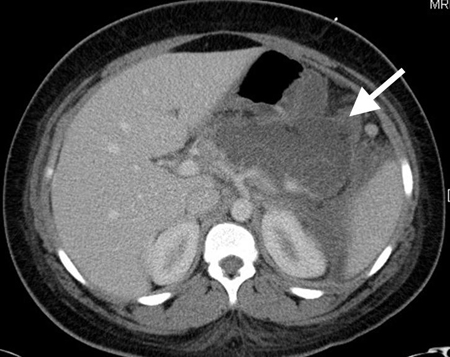
CT scan of teenage girl presenting with mid-epigastric abdominal pain as a result of gallstone pancreatitis. The large fluid collection in the pancreatic bed (white arrow) and lack of pancreatic enhancement suggest liquefactive necrosis of the pancreas
From the collection of Dr Kuojen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
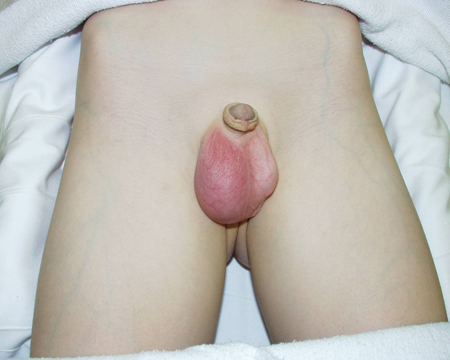
Young boy with right testicular pain. The testicle is swollen, tender, and erythematous as a result of torsion of the appendix testes. The clinical signs and symptoms mimic those of testicular torsion
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
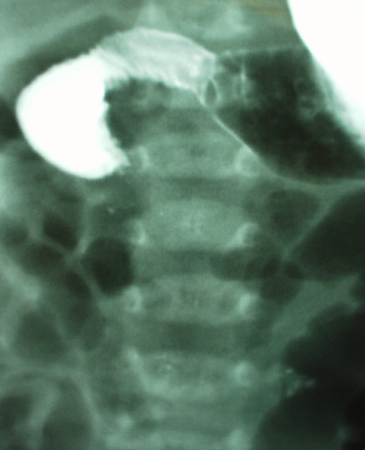
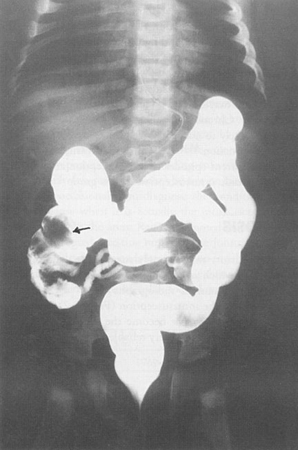
Contrast enema demonstrating ileocolic intussusception (black arrow)
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
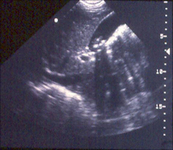
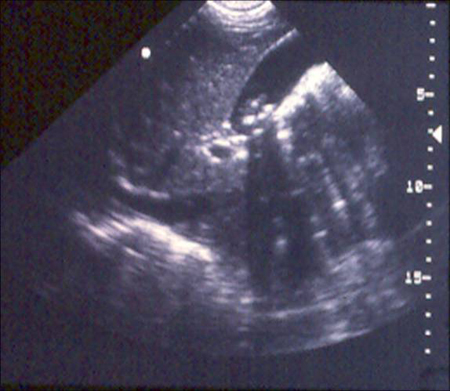
Gallbladder ultrasound demonstrating cholelithiasis with characteristic shadowing
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
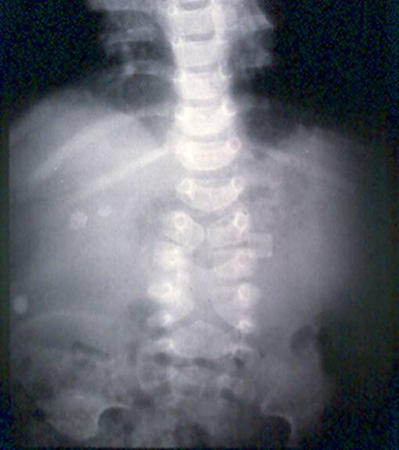
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
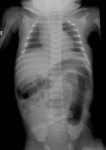
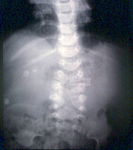
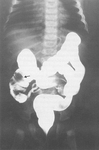
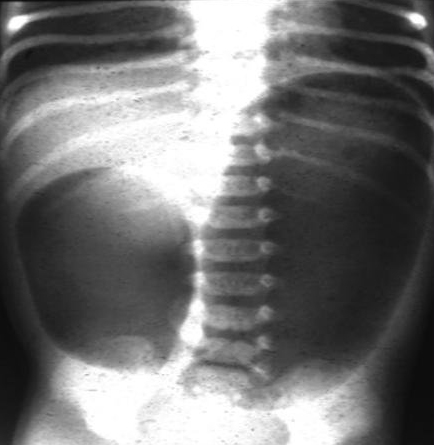
Abdominal x-ray demonstrating double bubble gas pattern consistent with duodenal atresia
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
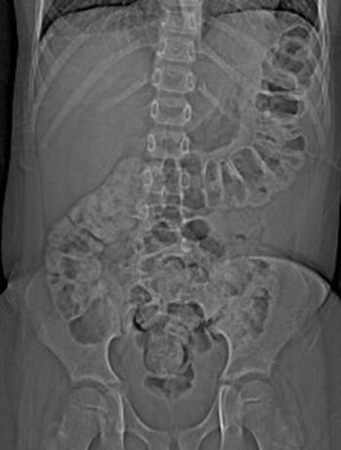
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
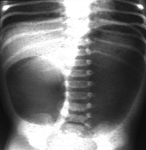
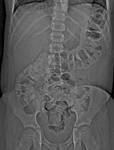
Abdominal x-ray of a young boy with acute, severe abdominal pain, demonstrating stool throughout the colon and rectum
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
Abdominal x-ray with opacities in the RUQ consistent with gallstones
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
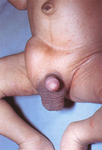
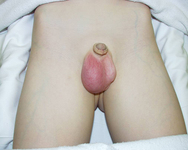
Infant boy with swollen, tender, and erythematous left testicle. The testicle is retracted consistent with testicular torsion
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
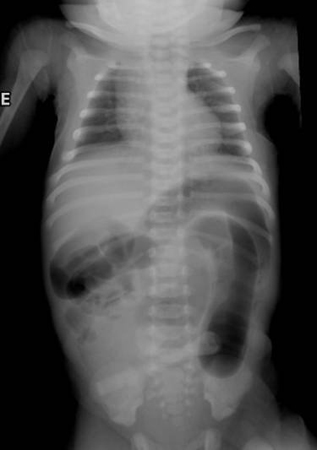
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
Abdominal x-ray of a neonate with abnormal stooling pattern and constipation. The dilated transverse and descending colon is suggestive of Hirschsprung's disease
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
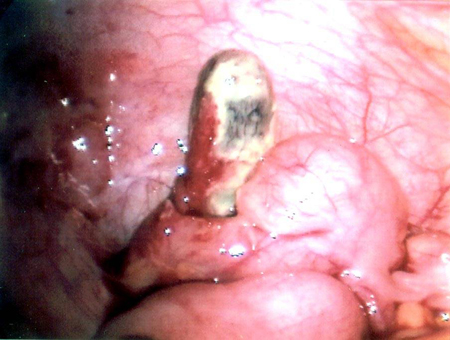
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
Necrotic appendix
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
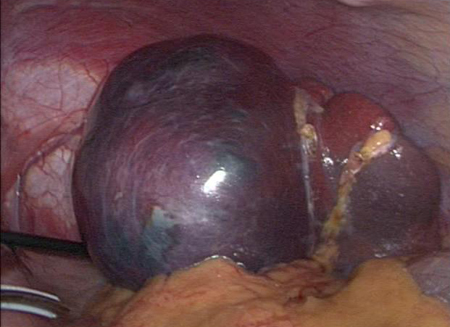
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
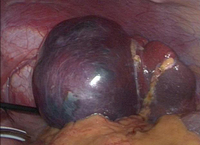
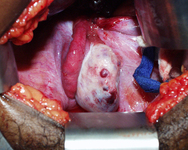
Intraoperative photo of large splenic cyst
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
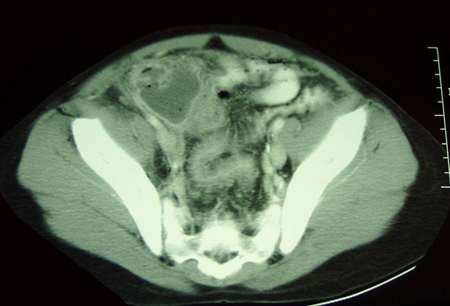
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
CT scan demonstrating intra-abdominal abscess consistent with perforated appendix
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
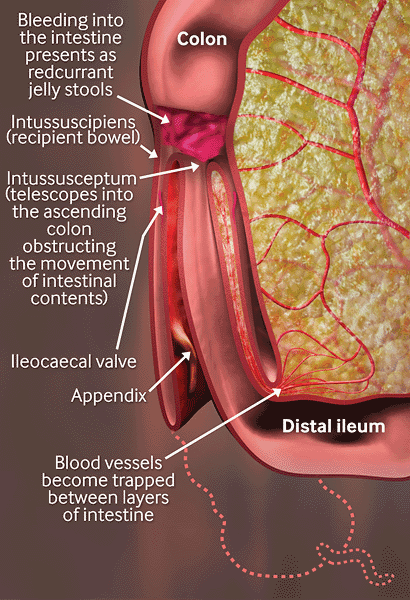
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
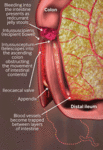
Intussusception: blood vessels become trapped between layers of intestine, leading to reduced blood supply, oedema, strangulation of bowel, and gangrene. Sepsis, shock, and death may eventually occur
Created by the BMJ Knowledge Centre
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
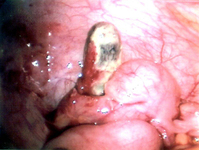
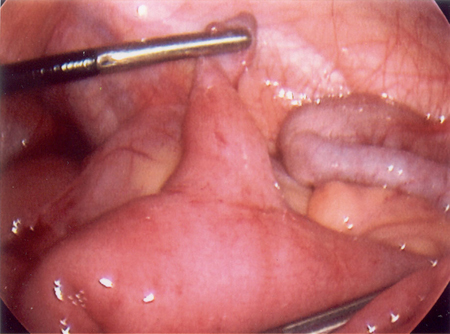
Intraoperative photo of Meckel's diverticulum
From the collection of Dr Kuojen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
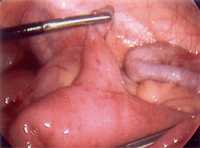
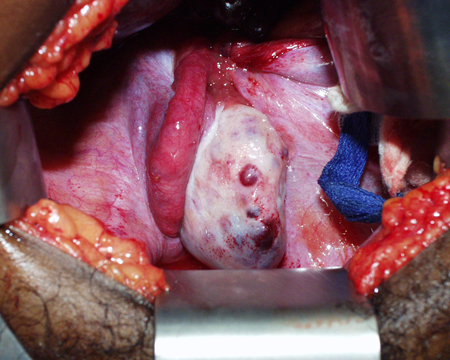
Intraoperative photo of ovarian mass that presented as ovarian torsion
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
CT scan demonstrating faecalith (white arrow) outside the lumen of the appendix consistent with perforated appendix
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
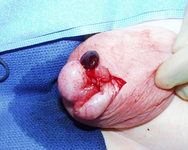
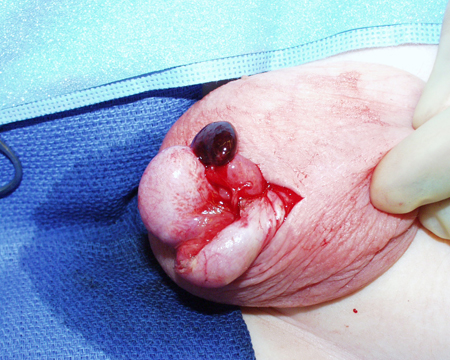
Torsion of an appendix testis resulting in acute infarction
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
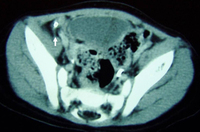
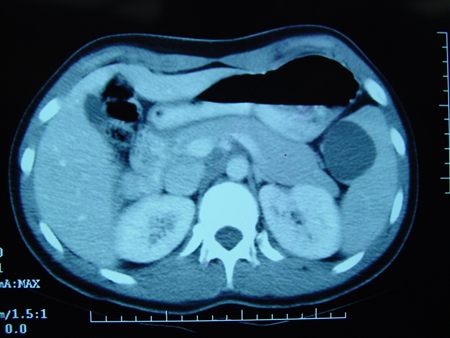
CT scan demonstrating fluid-filled cyst within the spleen
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Assessment of abdominal pain in children
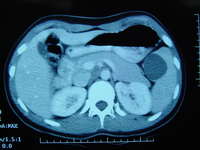
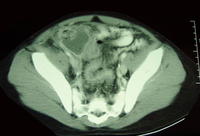
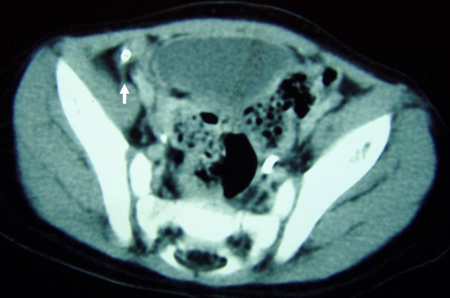
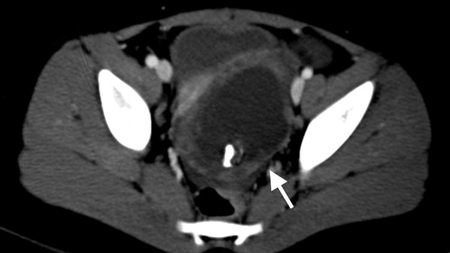
CT scan of a young girl presenting with ovarian torsion. The large pelvic cystic lesion contains calcifications (white arrow) consistent with a teratoma or dermoid cyst
From the collection of Dr KuoJen Tsao; used with permission
Veja esta imagem em contexto nas seguintes seções:
Vídeos
 Peripheral venous cannulation animated demonstration
Peripheral venous cannulation animated demonstrationHow to insert a peripheral venous cannula into the dorsum of the hand.
 Venepuncture and phlebotomy animated demonstration
Venepuncture and phlebotomy animated demonstrationHow to take a venous blood sample from the antecubital fossa using a vacuum needle.
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal