Summary
Definition
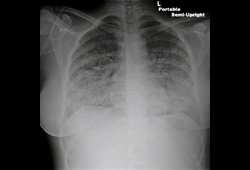
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- older age
- positive past medical history
- dyspnea
- pulmonary crepitations
- peripheral edema
- cool peripheries
- chest pain
- third heart sound (S3)
Other diagnostic factors
- fatigue and weakness or decreased exercise tolerance
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- elevated jugular venous pressure
- displaced apex beat (point of maximal impulse)
- dullness to percussion and decreased air entry in lung bases
- wheezing
- palpitations
- cough
- syncope
- murmur
- ascites
- hepatomegaly
- central cyanosis
Risk factors
- older age
- prior episode of heart failure
- coronary artery disease
- hypertension
- valvular heart disease
- pericardial disease
- myocarditis
- cardiac arrhythmias
- atrial fibrillation
- diabetes mellitus
- nonadherence to medications
- excessive salt intake
- excessive catecholamine stimulation
- abnormal thyroid function
- excessive alcohol intake
- obesity
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- ECG
- chest x-ray
- Hb
- thyroid function test
- B-type natriuretic peptide
- troponin
- echocardiography
- electrolyte panel with BUN, serum creatinine, glucose
- lipid profile
- liver function tests
Tests to consider
- lung ultrasound
- cardiac catheterization
- endomyocardial biopsy
- cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR)
- nuclear medicine imaging
- cardiac CT (coronary CT angiogram)
- additional biomarkers
Treatment algorithm
hemodynamically stable
hypotensive (systolic BP <90 mmHg)
hypertensive crisis
acute episode stabilized: LVEF <50%
acute episode stabilized: LVEF ≥50%
Contributors
Expert advisers
Syed Wamique Yusuf, MBBS, FACC, FRCPI
Professor of Medicine
Department of Cardiology
University of Texas
MD Anderson Cancer Center
Houston
TX
Disclosures
SWY declares that he was a co-director of the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Cardiovascular Board Review Course during which he had also delivered lectures.
Acknowledgements
Dr Syed Wamique Yusuf would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Daniel Lenihan, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
DL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Amal Mattu, MD
Professor of Medicine
Department of Emergency Medicine
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
AM declares that he has no competing interests.
David Whellan, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Jefferson Medical College
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
DW declares that he has no competing interests.
Katherine C. Wu, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Baltimore
MD
Disclosures
KCW declares that she has no competing interests.
Sanjay Sharma, BSc (Hons), FRCP (UK), MD
Consultant Cardiologist
King's College Hospital London
London
UK
Disclosures
SS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021 Sep 21;42(36):3599-726.Full text Abstract
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022 May 3;145(18):e895-1032.Full text Abstract
Ezekowitz JA, O'Meara E, McDonald MA, et al. 2017 comprehensive update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society guidelines for the management of heart failure. Can J Cardiol. 2017 Nov;33(11):1342-433.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
- Asthma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2023 focused update of the 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure
- 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure
More GuidelinesVideos
Central venous catheter insertion: animated demonstration
How to perform an ECG: animated demonstration
More videosPatient information
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation: what is it?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer