Resumo
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
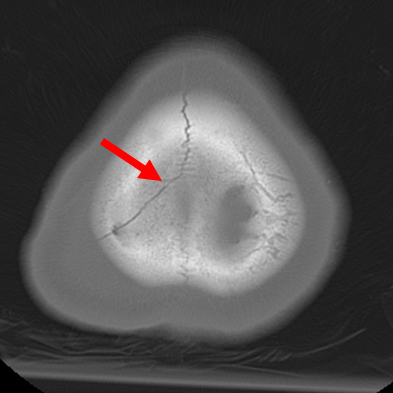
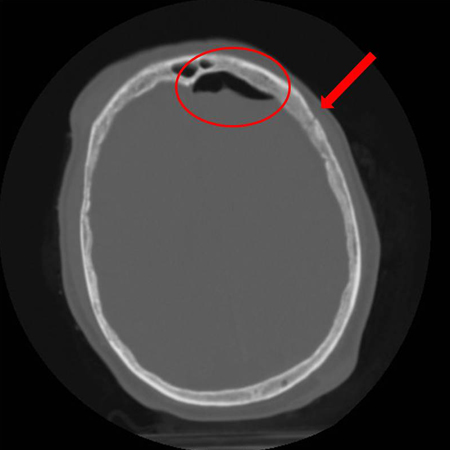
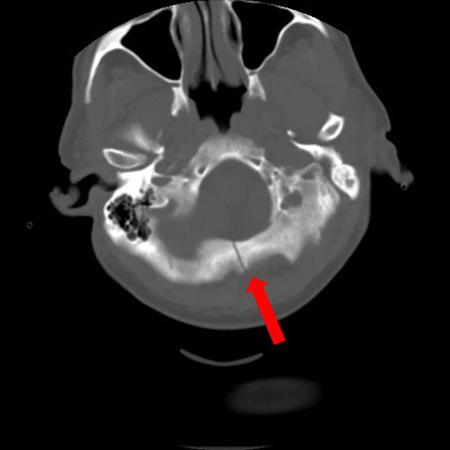
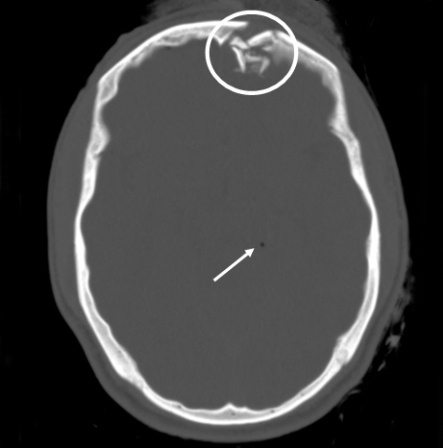
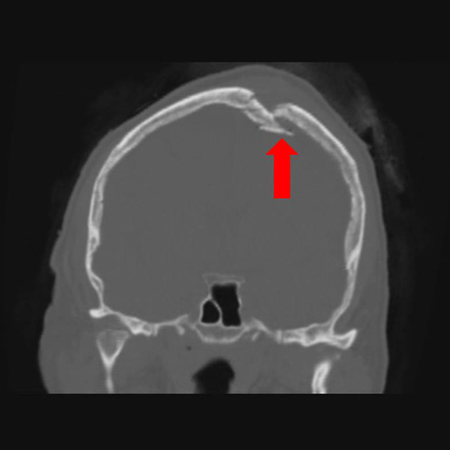
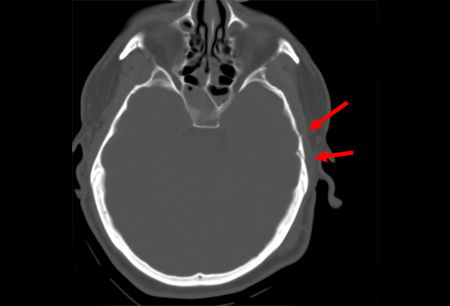
- open fracture
- palpable discrepancy in bone contour
- Battle sign
- periorbital ecchymosis
- bloody otorrhea
- cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea
- facial paralysis, nystagmus, or paresthesia
Other diagnostic factors
- evidence of trauma
- cranial pain or headache
- nausea
- altered mental state/loss of consciousness
- abnormal pupillary reflexes
- hearing loss
Risk factors
- fall from height
- motor vehicle accident
- assault resulting in head trauma
- gunshots to the head
- male sex
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
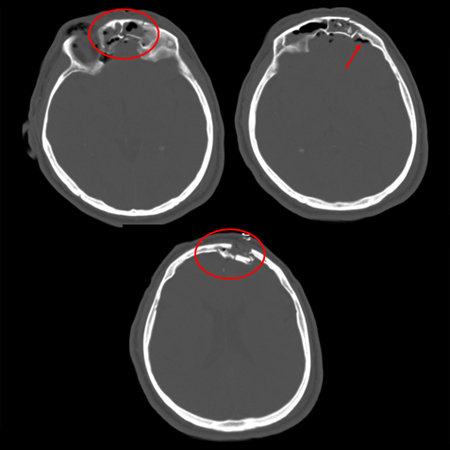
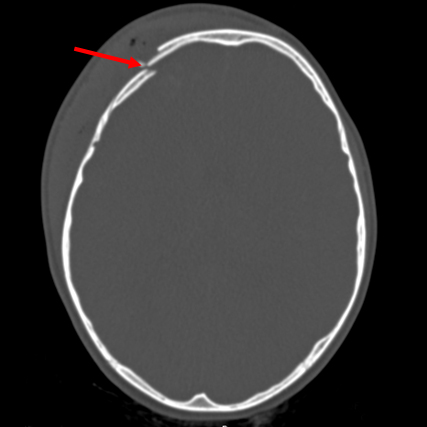
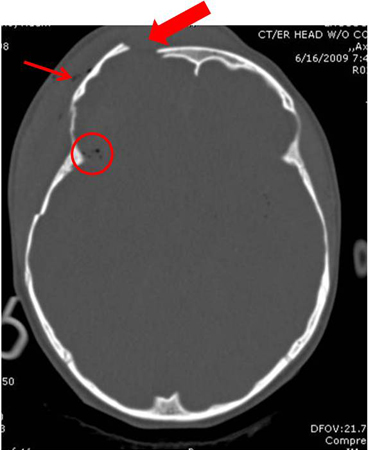
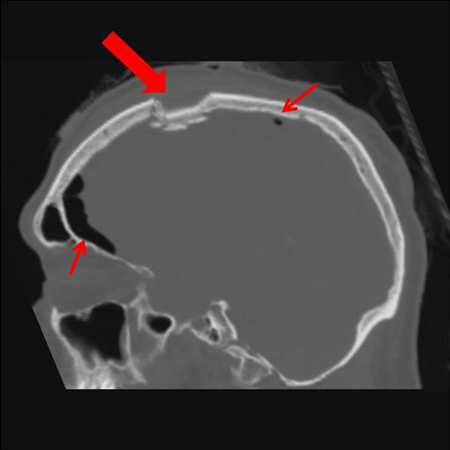
- cranial CT
Tests to consider
- beta-2 transferrin assay
- MRI brain
- MR angiography
- cranial ultrasound
- plain skull x-ray
- CT scan cervical spine
- skeletal survey
- CT angiogram
- CT venogram
Treatment algorithm
closed nondepressed fracture
closed depressed fracture
open fracture
persistent cranial nerve injury or CSF leakage
Contributors
Expert advisers
Demetrios Demetriades, MD, PhD, FACS
Professor of Surgery
Director
Division of Trauma and Surgical Intensive Care
LAC+USC Trauma Center
Keck School of Medicine at USC
University of Southern California
Los Angeles
CA
Disclosures
DD declares that he has no competing interests.
Leslie Kobayashi, MD, FACS
Professor of Surgery
Division of Trauma, Surgical Critical Care and Burns
University of California San Diego
San Diego
CA
Disclosures
LK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Prof Sherard Austin Tatum, MD
Professor Otolaryngology and Pediatrics
SUNY Upstate Medical University
Syracuse
New York
Disclosures
SAT declares that he has no competing interests.
Tunji Lasoye, FRCS, FCEM, MA, Med Ed
Consultant and Honorary Senior Lecturer in Emergency Medicine
Clinical Lead
Emergency Department
Director of Medical Education
King's College Hospital
London
UK
Disclosures
TL declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Expert Panel on Neurological Imaging: Shih RY, Burns J, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® head trauma: 2021 update. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021 May;18(5S):S13-36.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Suture lines in children
- Cephalhematoma
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- ACR Appropriateness Criteria: head trauma
- ACR Appropriateness Criteria: head trauma - child
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer