Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- unconventional behavior during history
- emotional processing problems
- recent psychological or physical stressors
- remote life stressors
- multiple illness behaviors
- unusual neurologic deficits
- give-way weakness
- inconsistent examination findings
- paradoxical sensory findings
- distractible symptoms
- generalized seizure-like motor movements without loss of awareness
- gait disorders
- functional movement disorders
Other diagnostic factors
- cognitive complaints
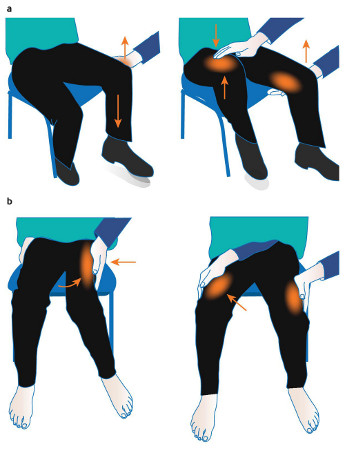
- Hoover sign
- speech disturbance
- swallowing disturbance
- pseudoclonus
- convergence spasm
Risk factors
- history of sexual or physical abuse
- adverse childhood events
- history of trauma-related disorders
- female sex
- alexithymia
- neuroticism
- previously poor doctor-patient relationships
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- laboratory testing
- electroencephalogram (EEG)
Tests to consider
- comprehensive neuropsychological testing
- standardized personality testing
- focused symptom inventories
Treatment algorithm
functional neurologic disorder
somatic symptom disorder
Contributors
Authors
Cynthia M. Stonnington, MD

Professor of Psychiatry
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale
AZ
Disclosures
CMS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Erika Driver-Dunckley, MD

Professor of Neurology
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale
AZ
Disclosures
EDD declares that she has no competing interests.
Katherine H. Noe, MD, PhD

Associate Professor of Neurology
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale
AZ
Disclosures
KHN declares that she has no competing interests.
Dona Locke, PhD

Professor of Psychology
Mayo Clinic
Scottsdale
AZ
Disclosures
DL declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
David Perez, MD, MMSc
Psychiatrist and Assistant Neurologist
Massachusetts General Hospital
Associate Professor of Neurology and Psychiatry
Harvard Medical School
Boston
MA
Disclosures
DLP has received honoraria for continuing medical education lectures in functional neurologic disorder, research funding for the NH and Sidney R. Baer Jr. Foundation, and royalties from Springer Nature for a textbook on functional movement disorder. DLP has also previously published with the BMJ and is on the editorial board of Epilepsy & Behavior. DLP is the author of a number of papers cited in this topic.
James L Levenson, MD
Rhona Arenstein Professor of Psychiatry
Virginia Commonwealth University
Virginia
Disclosures
JLL declares that he was the unpaid text editor for the sections of DSM 5 and DSM 5-TR covering the two diagnoses listed in the topic.
Anton Scamvougeras, MBChB, FRCP
Consultant Neuropsychiatrist and Associate Clinical Professor
Department of Psychiatry
University of British Columbia
Vancouver
British Columbia
Canada
Disclosures
AS declares that he has no competing interests. AS is the author of one paper cited in the topic.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Perez DL, Aybek S, Popkirov S, et al; American Neuropsychiatric Association Committee on Research. A review and expert opinion on the neuropsychiatric assessment of motor functional neurological disorders. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021 Winter;33(1):14-26.Full text Abstract
Löwe B, Levenson J, Depping M, et al. Somatic symptom disorder: a scoping review on the empirical evidence of a new diagnosis. Psychol Med. 2022 Mar;52(4):632-48.Full text Abstract
Stone J, Burton C, Carson A. Recognising and explaining functional neurological disorder. BMJ. 2020 Oct 21;371:m3745.
Bennett K, Diamond C, Hoeritzauer I, et al. A practical review of functional neurological disorder (FND) for the general physician. Clin Med (Lond). 2021 Jan;21(1):28-36.Full text Abstract
Baslet G, Bajestan SN, Aybek S, et al. Evidence-based practice for the clinical assessment of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures: a report from the American Neuropsychiatric Association Committee on Research. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2021 Winter;33(1):27-42.Full text Abstract
den Boeft M, Claassen-van Dessel N, van der Wouden JC. How should we manage adults with persistent unexplained physical symptoms? BMJ. 2017 Feb 8;356:j268. Abstract
Henningsen P, Zipfel S, Herzog W. Management of functional somatic syndromes. Lancet. 2007 Mar 17;369(9565):946-55. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Illness anxiety disorder
- Body dysmorphic disorder
- Factitious disorder
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- A review and expert opinion on the neuropsychiatric assessment of motor functional neurological disorders
- Evidence-based practice for the clinical assessment of psychogenic nonepileptic seizures
More GuidelinesLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer