Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- spiking fever
- neck pain or torticollis
- odynophagia
- dysphagia
- neck swelling/mass/lymphadenopathy
- oropharyngeal swelling
- drooling
Other diagnostic factors
- decreased oral intake
- anorexia
- malaise
- irritability
- trismus
- dysphonia
- dyspnea
- fatigue
- sleep apnea
- stridor
- tonsillar swelling
- increased respiration rate
- decreased oxygen saturations
- cyanosis
- tachypnea
- tracheal tug
- intercostal recession
Risk factors
- foreign body ingestion
- trauma to posterior pharyngeal wall
- dental caries/infection
- diabetes mellitus
- male sex
- adenotonsillectomy
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CBC
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CT neck with contrast
- x-ray of neck
- ultrasonography of neck
- examination under anesthetic (EUA)
- culture
Treatment algorithm
airway compromise
no airway compromise
Contributors
Authors
Carl Philpott, MB ChB, FRCS (ORL-HNS) DLO, MD, PGCME

Consultant in ENT & Rhinology
James Paget University Hospital
Great Yarmouth
UK
Disclosures
CP is an advisory board member for GSK, Sanofi, and Stryker. He has received grants from NIHR and is a trustee of Fifth Sense. CP is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Kala Kumaresan, MBBS, MRCS (ENT)
Clinical Research Fellow
Department of ENT
James Paget University Hospital
Norwich
UK
Disclosures
KK declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Professor Carl Philpott and Dr Kala Kumaresan would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Kristian Hutson, Dr Lorna Langstaff, Dr Asad Qayyum, Dr Kevin Kulendra, Dr Cameron Davies-Husband, and Dr Marcos Martinez Del Pero, previous contributors to this topic.
Divulgaciones
KH, LL, AQ, KK, CDH, and MMDP declare that they have no competing interests.
Revisores por pares
Remco de Bree, MD, PhD
Otolaryngologist
Head and Neck Surgeon
VU University Medical Center
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Divulgaciones
RdB declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael Johns, MD
Director
Assistant Professor
Emory University
Atlanta
GA
Declarações
MJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Lynn Solomon, MD
Assistant Professor
Tufts University
Boston
MA
Declarações
LS declares that she has no competing interests.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Philpott CM, Selvadurai D, Banerjee AR. Paediatric retropharyngeal abscess. J Laryngol Otol. 2004 Dec;118(12):919-26. Resumo
Bochner RE, Gangar M, Belamarich PF. A clinical approach to tonsillitis, tonsillar hypertrophy, and peritonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses. Pediatr Rev. 2017 Feb;38(2):81-92. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
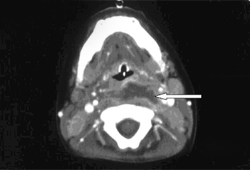
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Acute epiglottitis
- Laryngotracheobronchitis
- Meningitis
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- A clinical approach to tonsillitis, tonsillar hypertrophy, and peritonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Sore throat
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal