Resumen
Definición
Anamnesis y examen
Principales factores de diagnóstico
- oral ulcers
- afebrile
- absence of genital or ocular ulceration
- no history of immunodeficiency
- absence of pallor
Factores de riesgo
- positive family history
- nonsmoker or cessation of smoking
- trauma
- age <30 years
- cows' milk-fed children
- female sex
- high stress levels
- food intolerance
- hormonal imbalance
- use of sodium lauryl sulfate-containing toothpaste
Pruebas diagnósticas
Pruebas diagnósticas que deben considerarse
- CBC
- serum ferritin
- serum folate
- serum vitamin B12
- serum IgA-tTG
- viral serology (e.g. HIV or Epstein-Barr virus)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate and CRP
- biopsy
- antinuclear antibody test
- serum HIV test
Algoritmo de tratamiento
all patients
Colaboradores
Autores
Jennifer Taylor, BDS, MFDS RCS, MBChB FDS (OM), PhD
Consultant and Honorary Senior Lecturer in Oral Medicine
Glasgow Dental Hospital and School
Glasgow
Scotland
UK
Divulgaciones
JT declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimientos
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the late Professor Crispian Scully for his contribution to this topic.
Revisores por pares
James J. Sciubba, DMD, PhD
Consultant for Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine
The Milton J. Dance Head and Neck Center
Greater Baltimore Medical Center
Baltimore
MD
Divulgaciones
JJS declares that he has no competing interests.
Pepe Shirlaw, BDS, FDS RCPS
Consultant in Oral Medicine
Guy’s Hospital
Great Maze Pond
London
UK
Divulgaciones
PS declares that she has no competing interests.
Agradecimiento de los revisores por pares
Los temas de BMJ Best Practice se actualizan de forma continua de acuerdo con los desarrollos en la evidencia y en las guías. Los revisores por pares listados aquí han revisado el contenido al menos una vez durante la historia del tema.
Divulgaciones
Las afiliaciones y divulgaciones de los revisores por pares se refieren al momento de la revisión.
Referencias
Artículos principales
Scully C. Clinical practice. Aphthous ulceration. N Engl J Med. 2006 Jul 13;355(2):165-72. Resumen
Scully C, Gorsky M, Lozada-Nur F. The diagnosis and management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a consensus approach. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003 Feb;134(2):200-7. Resumen
Brocklehurst P, Tickle M, Glenny AM, et al. Systemic interventions for recurrent aphthous stomatitis (mouth ulcers). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD005411.Texto completo Resumen
Artículos de referencia
Una lista completa de las fuentes a las que se hace referencia en este tema está disponible para los usuarios con acceso a todo BMJ Best Practice.
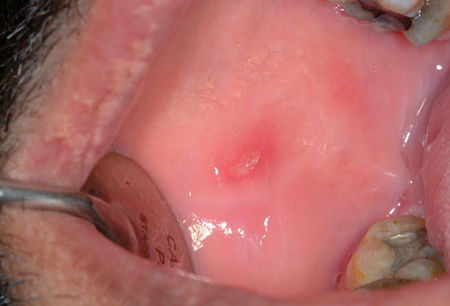
Diferenciales
- Behcet syndrome
- Malignant ulcer
- Folate deficiency
Más DiferencialesGuías de práctica clínica
- The diagnosis and management of recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a consensus approach
Más Guías de práctica clínicaFolletos para el paciente
Canker sores
Más Folletos para el pacienteInicie sesión o suscríbase para acceder a todo el BMJ Best Practice
El uso de este contenido está sujeto a nuestra cláusula de exención de responsabilidad