Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- fatigue
- anorexia
- weight loss
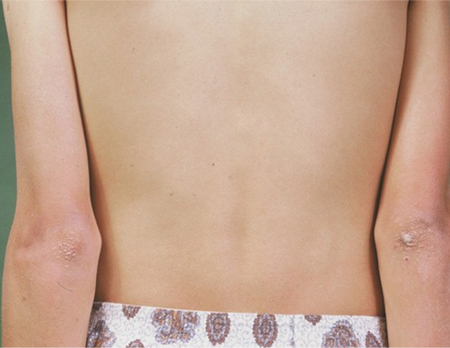
- hyperpigmentation
- acute circulatory collapse with hypotension and tachycardia
- salt craving
Other diagnostic factors
- gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain)
- postural hypotension
- arthralgia and myalgia
- axillary and pubic hair loss in women
Risk factors
- female sex
- adrenocortical autoantibodies
- adrenal hemorrhage
- autoimmune diseases
- celiac disease
- tuberculosis (TB)
- non-TB bacterial infection
- fungal infection
- HIV
- drugs that inhibit cortisol production
- metastatic malignancy
- sarcoidosis
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- morning serum cortisol
- plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
- serum electrolytes
- BUN and creatinine
- CBC
Tests to consider
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test
- plasma renin activity
- serum aldosterone
- serum dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S)
- adrenal antibodies
- adrenal CT or MRI
- insulin hypoglycemia test
- overnight single-dose metyrapone test
Treatment algorithm
adrenal crisis
minor intercurrent stress
severe intercurrent stress
stable and/or after treatment of acute episode
Contributors
Authors
Laleh Razavi Nematollahi, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Clinical and Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism
University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center
Case Western Reserve University
Cleveland
OH
Disclosures
LRN declares that she has no competing interests.
Baha Arafah, MD
Chief, Division of Endocrinology
University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center
Case Western Reserve University
Cleveland
OH
Disclosures
BA declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Laleh Razavi Nematollahi and Dr Baha Arafah would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr T. Joseph McKenna, Dr Shehzad Basaria, and Dr Milena Braga-Basaria, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
TJM, SB, and MBB declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Rajesh K. Garg, MD
Instructor in Medicine
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Division of Endocrinology
Diabetes and Hypertension
Boston
MA
Disclosures
RKG declares that he has no competing interests.
Antoine Tabarin, MD
Head
Department of Endocrinology
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Bordeaux
Pessac
France
Disclosures
AT declares that he has no competing interests.
Blandine Gatta-Cherifi, MD
Department of Endocrinology
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Bordeaux
Pessac
France
Disclosures
BGC declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Bornstein SR, Allolio B, Arlt W, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of primary adrenal insufficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Feb;101(2):364-89.Full text Abstract
Husebye ES, Pearce SH, Krone NP, et al. Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet. 2021 Feb 13;397(10274):613-29. Abstract
Betterle C, Presotto F, Furmaniak J. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Addison's disease in adults. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019 Dec;42(12):1407-33. Abstract
Arlt W; Society for Endocrinology Clinical Committee. Society For Endocrinology endocrine emergency guidance: emergency management of acute adrenal insufficiency (adrenal crisis) in adult patients. Endocr Connect. 2016 Sep;5(5):G1-3.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Adrenal suppression due to the use of glucocorticoid or other drugs with glucocorticoid activity (e.g., medroxyprogesterone acetate therapy)
- Central (secondary or tertiary) adrenal insufficiency (pituitary or hypothalamic lesions)
- Hemochromatosis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Adrenal insufficiency & Addison’s disease
- Emergency management of acute adrenal insufficiency (adrenal crisis) in adult patients
More GuidelinesPatient information
Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison disease): what is it?
Primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison disease): what are the treatment options?
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer