Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- personal or family history of psoriasis
- joint pain and stiffness
- peripheral arthritis
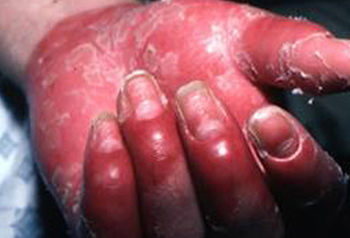
- dactylitis
- history of scalp or nail problems
Other diagnostic factors
- enthesitis
- spinal stiffness
- reduction of cervical spine mobility
- uveitis
- inflammatory bowel disease
Risk factors
- psoriasis
- family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis
- history of joint or tendon trauma
- infection
- smoking
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- plain film radiographs of the hands and feet
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP)
- rheumatoid factor
- anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody
- lipid profile
- fasting blood glucose
- uric acid level
- synovial fluid aspiration and analysis
Tests to consider
- plain film radiographs of the spine and pelvis
- MRI scan of sacroiliac joints
Emerging tests
- joint ultrasound
Treatment algorithm
peripheral arthritis
axial disease
enthesitis
dactylitis
Contributors
Authors
Siba P. Raychaudhuri, MD, FACP, FACR
Professor
Director, Department of Medicine/ Rheumatology, Allergy, and Clinical Immunology
University of California Davis School of Medicine
Sacramento
CA
Disclosures
SPR declares that he has received research grants, prepared research papers, and attended board meetings for Sun Pharmacy, AbbVie Pharmacy, Novartis Pharma, Johnson and Johnson, the National Psoriasis Foundation, and the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). SPR is the author of some of the references cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Siba P. Raychaudhuri would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Clement J. Michet, previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
CJM is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Revisores
Philip S. Helliwell, MD, PhD
Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology
University of Leeds
Leeds
UK
Declarações
PSH is an author of some references cited in this topic.
Luis R. Espinoza, MD
Professor and Chief
Section of Rheumatology
Department of Internal Medicine
LSU Health Sciences Center
New Orleans
LA
Declarações
LRE declares that he has no competing interests.
William J. Taylor, PhD, MBChB, FAFRM, FRACP
Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
University of Otago, Wellington
Wellington
New Zealand
Declarações
WJT is an author of some references cited in this topic.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Singh JA, Guyatt G, Ogdie A, et al. 2018 American College of Rheumatology/National Psoriasis Foundation guideline for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Jan;71(1):5-32.Texto completo Resumo
Gossec L, Baraliakos X, Kerschbaumer A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jun;79(6):700-12.Texto completo Resumo
Coates LC, Soriano ER, Corp N, et al; GRAPPA Treatment Recommendations domain subcommittees. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Aug;18(8):465-79.Texto completo Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Gout
- Erosive osteoarthritis
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- 2022 American College of Rheumatology guideline for vaccinations in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases
- EULAR points to consider for therapeutic drug monitoring of biopharmaceuticals in inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases
Mais DiretrizesFolhetos informativos para os pacientes
Gout
Psoriasis: what is it?
Mais Folhetos informativos para os pacientesConectar-se ou assinar para acessar todo o BMJ Best Practice
O uso deste conteúdo está sujeito ao nosso aviso legal