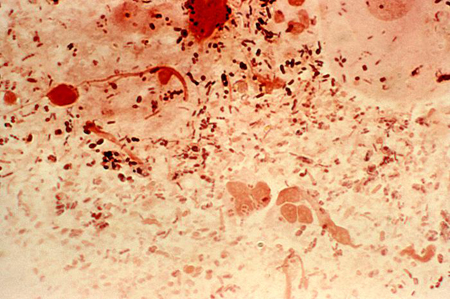
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- urethral discharge in men
- tenderness and/or swelling of the epididymis
- mucopurulent or purulent exudate at the endocervix
Other diagnostic factors
- pelvic pain in women
- urethral irritation in men
- dysuria in men
- tenderness and/or swelling of testis
- tenderness and/or swelling of prostate
- anal pruritus
- mucopurulent discharge from the rectum
- rectal pain
- tenesmus
- rectal bleeding
- vaginal discharge
- cervical friability
- uterine, adnexal, or cervical motion tenderness
- uterine mass
- anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
- conjunctivitis
- fever
- skin lesions (papules, bullae, petechiae, or necrotic) at extremities
- polyarthritis
- purpuric rash
- positive Brudzinski and Kernig sign
- seizures
- focal cerebral signs
- murmur
- ophthalmia neonatorum
- rhinitis
- urethritis (infantile)
- vaginitis
Risk factors
- age 20 to 24 years
- men who have sex with men (MSM)
- black ancestry
- current or prior history of STI
- multiple recent sex partners
- inconsistent condom use
- risk factors of partner
- history of sexual or physical abuse
- substance use
- past incarceration
- high-morbidity community
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT)
- culture
- urinalysis in men
- Gram stain of urine sediment
- Gram stain of urethral discharge
- HIV test
- syphilis test
Tests to consider
- transvaginal ultrasound
- pelvic CT/MRI
Treatment algorithm
nonpregnant >45 kg: urogenital/anorectal or pharyngeal infection (excluding complicated genitourinary infection)
nonpregnant >45 kg: complicated genitourinary infection
nonpregnant >45 kg: disseminated gonococcal infection
pregnant: uncomplicated urogenital/anorectal or pharyngeal infection (excluding complicated genitourinary infection)
pregnant: complicated infection
neonate
child ≤45 kg
recurrent/resistant: urogenital/anorectal infection or pharyngitis
Contributors
Authors
Sheldon Morris, MD, MPH
Assistant Professor
Division of Infectious Diseases
Department of Medicine
UCSD Antiviral Research Center
Division of Family Medicine
Department of Family and Preventive Medicine
UCSD La Jolla Family and Sports Medicine
San Diego
CA
Disclosures
SM has received research funding via his institution from Merck, Gilead Sciences, National Institutes of Health, California HIV/AIDS Research Program, and California Institute for Regenerative Medicine. He has completed a National Institutes of Health contract for research study on the Visby Medical Sexual Health Test. He holds stock in Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer. He is a co-founder of Aspera Biomedicines and a consultant for Primmune Therapeutics. SM is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Vani Dandolu, MD, MPH
Associate Professor
Ob/Gyn and Urology
Director
Division of Urogynecology
Associate Residency Program Director
Temple University Hospital
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
VD declares that he has no competing interests.
Eva Jungmann, FRCP MSc
Consultant in Genitourinary and HIV Medicine
Archway Centre & Mortimer Market Centre
London
UK
Disclosures
EJ declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonococcal isolate surveillance project (GISP). 30 August 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021 Jul 23;70(4):1-187.Full text Abstract
Miller WC, Ford CA, Morris M, et al. Prevalence of chlamydial and gonococcal infections among young adults in the United States. JAMA. 2004 May 12;291(18):2229-36.Full text Abstract
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae - 2014. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2014;63(RR-02):1-19.Full text Abstract
Fifer H, Saunders J, Soni S, et al. 2018 UK national guideline for the management of infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Int J STD AIDS. 2020 Jan;31(1):4-15.Full text Abstract
US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021 Sep 14;326(10):949-56.Full text Abstract
World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. 2016 [internet publication].Full text
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance on the use of expedited partner therapy in the treatment of gonorrhea. 18 August 2021 [internet publication].Full text
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
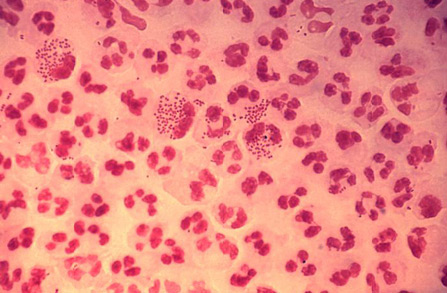
Differentials
- Chlamydia infection
- Trichomonas
- Other infectious causes of urethritis, cervicitis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and epididymitis
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- Reducing sexually transmitted infections
- Guidance on the use of expedited partner therapy in the treatment of gonorrhea
More GuidelinesPatient information
Gonorrhea
More Patient informationVideos
Intramuscular injection animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer