Resumo
Definição
História e exame físico
Principais fatores diagnósticos
- family history of autosomal-dominant PKD (ADPKD) or end-stage renal disease
- family history of cerebrovascular event
- renal cysts
- hypertension
- abdominal/flank pain
- hematuria
- palpable kidneys/abdominal mass
- headaches
- dysuria, suprapubic pain, fever
Outros fatores diagnósticos
- cardiac murmur
- abdominal hernia
- hepatomegaly
- chest pain
Fatores de risco
- family history of autosomal-dominant PKD (ADPKD)
- family history of cerebrovascular event
Investigações diagnósticas
Primeiras investigações a serem solicitadas
- renal ultrasound
- CT abdomen/pelvis
- MRI abdomen/pelvis
- urinalysis/Gram stain and urine culture
- serum electrolytes, BUN, creatinine
- fasting lipid profile
- ECG
- CT brain
Investigações a serem consideradas
- genetic testing
- echocardiogram
- 24-hour urine collection
- dual-energy CT of abdomen/pelvis
- lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis
- C-reactive protein
- PET scan
Algoritmo de tratamento
confirmed autosomal-dominant polycystic disease
end-stage renal disease
Colaboradores
Autores
Marie C. Hogan, MD, PhD
Consultant
Division of Nephrology
Professor of Medicine
College of Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Declarações
MCH receives research funding from Novartis, and was an investigator participating in tolvaptan clinical trials. MCH is also an author of several references cited in this topic.
Maria Irazabel Mira, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine, Associate Consultant
Division of Nephrology and Hypertension
Department of Internal Medicine
Mayo Clinic
Rochester
MN
Declarações
MIM is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Agradecimentos
Dr Marie C Hogan and Dr Maria Irazabal Mira would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Vicente Torres, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures: VT is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Revisores
Richard Sandford, PhD, FRCP
Wellcome Trust Senior Fellow in Clinical Research
University Reader in Real Genetics
Honorary Consultant in Medical Genetics
Cambridge
UK
Declarações
RS declares that he has no competing interests.
Arlene Chapman, MD
Professor of Medicine
Renal Division
Emory University
School of Medicine
Atlanta
GA
Declarações
Not disclosed.
Créditos aos pareceristas
Os tópicos do BMJ Best Practice são constantemente atualizados, seguindo os desenvolvimentos das evidências e das diretrizes. Os pareceristas aqui listados revisaram o conteúdo pelo menos uma vez durante a história do tópico.
Declarações
As afiliações e declarações dos pareceristas referem--se ao momento da revisão.
Referências
Principais artigos
Bergmann C, Guay-Woodford LM, Harris PC, et al. Polycystic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018 Dec 6;4(1):50.Texto completo Resumo
Cornec-Le Gall E, Alam A, Perrone RD. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2019 Mar 2;393(10174):919-35. Resumo
Pei Y, Obaji J, Dupuis A, et al. Unified criteria for ultrasonographic diagnosis of ADPKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Jan;20(1):205-12.Texto completo Resumo
Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, et al; TEMPO 3:4 Trial Investigators. Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2012 Dec 20;367(25):2407-18.Texto completo Resumo
Schrier RW, Abebe KZ, Perrone RD, et al; HALT-PKD Trial Investigators. Blood pressure in early autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 11;371(24):2255-66. Resumo
Torres VE, Abebe KZ, Chapman AB, et al; HALT-PKD Trial Investigators. Angiotensin blockade in late autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 11;371(24):2267-76. Resumo
Artigos de referência
Uma lista completa das fontes referenciadas neste tópico está disponível para os usuários com acesso total ao BMJ Best Practice.
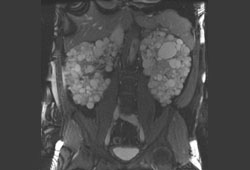
Diagnósticos diferenciais
- Acquired cystic kidney disease
- Simple cyst
- Tuberous sclerosis complex
Mais Diagnósticos diferenciaisDiretrizes
- Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): executive summary
Mais DiretrizesPatient information
Kidney infection
Kidney stones
More Patient informationCalculators
Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimate by the IDMS-Traceable MDRD Study Equation
More CalculatorsVideos
Diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults: animated demonstration
More videosLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer