Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- headache
- photophobia
- loss of consciousness
- third cranial nerve palsy
Other diagnostic factors
- age >50 years
- female sex
- black people
- nausea/vomiting
- altered mental status
- meningismus
- unilateral or bilateral sixth cranial nerve palsies
- intraocular hemorrhage
- focal neurologic deficits
- seizures
Risk factors
- hypertension
- smoking
- family history
- autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
- alcohol use
- cocaine use
- Marfan syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- pseudoxanthoma elasticum
- neurofibromatosis type I
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
- CT head
- CBC
- clotting profile
- serum electrolytes
- troponin I
- serum glucose
- ECG
Tests to consider
- lumbar puncture (LP)
- digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
- computed tomography angiography (CTA)
- magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Treatment algorithm
all patients
Contributors
Expert advisers
Salah Keyrouz, MD, FAHA, FCCM
Professor
Neurology and Neurosurgery
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis
MO
Disclosures
SK is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Acknowledgements
Dr Salah Keyrouz would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Michael N. Diringer, a previous contributor to this topic.
Disclosures
MND is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Venkatesh Aiyagari, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation
University of Illinois at Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
VA declares that he has no competing interests.
Peter Martin, MA, BM BCh, MD, FRCP
Consultant Neurologist
Addenbrookes Hospital
Cambridge
UK
Disclosures
PM declares that he has no competing interests.
Giovanni Grasso, M.D., PhD
Aggregate Professor of Neurosurgery
Neurosurgical Clinic
Department of Clinical Neuroscience
University of Palermo
Palermo
Italy
Disclosures
GG declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015 Aug;46(8):2368-400.Full text Abstract
Steiner T, Juvela S, Unterberg A, et al. European Stroke Organization guidelines for the management of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013 Feb 7;35(2):93-112.Full text Abstract
Hoh BL, Ko NU, Amin-Hanjani S, et al. 2023 Guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023 Jul;54(7):e314-70.Full text Abstract
Treggiari MM, Rabinstein AA, Busl KM, et al. Guidelines for the neurocritical care management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. 2023 Aug;39(1):1-28. Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
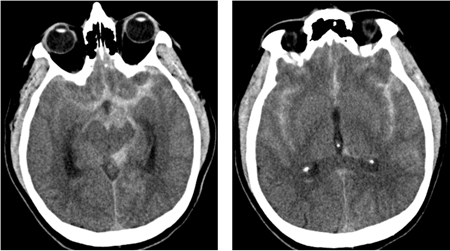
Differentials
- Nonaneurysmal perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Arterial dissection
- Cerebral and cervical arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2023 guideline for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Guidelines for the neurocritical care management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
More GuidelinesVideos
Diagnostic lumbar puncture in adults: animated demonstration
Tracheal intubation: animated demonstration
More videosPatient information
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer