Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
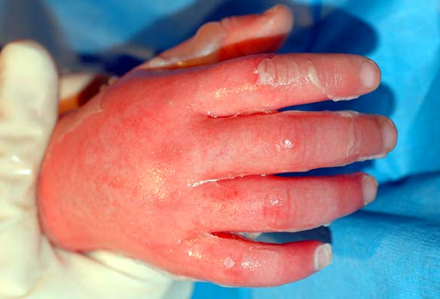
- erythema
- dry and painful burns
- wet and painful burns
- dry and insensate burns
- burns affecting subcutaneous tissue, tendon, or bone
- cellulitis
- clouded cornea
Risk factors
- young children
- age >60 years
- female sex (thermal burns)
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- complete blood count
- metabolic panel
- carboxyhemoglobin
- arterial blood gas
- fluorescein staining
- computed tomography scan of head and spine
- wound biopsy culture
- wound histology
Treatment algorithm
suitable for outpatient care
requires inpatient care
Contributors
Authors
Rob Sheridan, MD
Professor of Surgery
Harvard Medical School
Cambridge
MA
Disclosures
RS is an author of a number of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
Ravi Ubriani, MD, FAAD
Assistant Professor of Clinical Dermatology
Columbia University
New York
NY
Disclosures
RU declares that he has no competing interests.
Chris Tedeschi, MD
Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine
Department of Emergency Medicine
New York-Presbyterian Hospital
New York
NY
Disclosures
CT declares that he has no competing interests.
Chad M. Hivnor, Major, USAF, MC, FS
Chief
Outpatient & Pediatric Dermatology
59th Medical Wing/ SGOMD
Lackland Air Force Base
San Antonio
TX
გაფრთხილება:
CMH declares that he has no competing interests.
Dean D. Ad-El, MD
Chairman, Department of Plastic Surgery and Burn Unit
Rabin Medical Center - Beilinson Hospital
Sackler Faculty of Medicine
Tel-Aviv University
Director of Plastic Surgery Services
Schneider Children's Medical Center of Israel
Petach Tikvah
Israel
გაფრთხილება:
DDAE participated as one of the moderators in a course in IMCAS, Paris in January 2009.
რეცენზენტების განცხადებები
BMJ Best Practice-ის თემების განახლება სხვადასხვა პერიოდულობით ხდება მტკიცებულებებისა და რეკომენდაციების განვითარების შესაბამისად. ქვემოთ ჩამოთვლილმა რეცენზენტებმა თემის არსებობის მანძილზე კონტენტს ერთხელ მაინც გადახედეს.
გაფრთხილება
რეცენზენტების აფილიაციები და გაფრთხილებები მოცემულია გადახედვის მომენტისთვის.
წყაროები
ძირითადი სტატიები
American Burn Association. Advanced burn life support course: provider manual 2018 update. 2018 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies. International first aid, resuscitation, and education guidelines. 2020 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
American Burn Association, American College of Surgeons. Guidelines for the operation of burn centers. J Burn Care Res. 2007 Jan-Feb;28(1):134-41. აბსტრაქტი
Cartotto R, Johnson LS, Savetamal A, et al. American Burn Association Clinical Practice Guidelines on burn shock resuscitation. J Burn Care Res. 2024 May 6;45(3):565-89.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
გამოყენებული სტატიები
ამ თემაში მოხსენიებული წყაროების სრული სია ხელმისაწვდომია მომხმარებლებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ წვდომა BMJ Best Practice-ის ყველა ნაწილზე.
დიფერენციული დიაგნოზები
- Rash in children
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
მეტი დიფერენციული დიაგნოზებიგაიდლაინები
- International first aid and resuscitation guidelines
- Management of burns in pre-hospital trauma care
მეტი გაიდლაინებიპაციენტის ბროშურები
Burns
მეტი პაციენტის ბროშურებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას