Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- history of trauma or osteoporosis
- wrist pain
- tenderness over the distal radius
- swelling
Other diagnostic factors
- deformity
- tenderness in the anatomic snuff-box
- numbness in the fingers
- hypoesthesia
- open wound
- absent pulse
Risk factors
- trauma
- osteoporosis
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
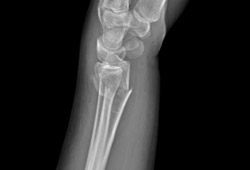
- plain radiographs of the wrist
Tests to consider
- CT wrist
- MRI (without contrast) wrist
- dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
Treatment algorithm
closed
open
isolated fracture of distal radius
isolated scaphoid fracture
concomitant distal radius and scaphoid or ulnar styloid fractures
confirmed wrist fracture
Contributors
Expert advisers
Niels W.L. Schep, MD
Trauma, Hand and Wrist Surgeon
Department of Trauma and Hand Surgery
Maasstad Hospital
Rotterdam
Netherlands
Disclosures
NS declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Niels W.L. Schep would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Jeffrey N. Lawton, Dr John R. Lien, Dr Gregory D. Byrda, Dr Tamara D. Rozental, and Dr Chaitanya S. Mudgal, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
JNL is a consultant for Innomed Inc, has received honoraria from The AO Foundation for teaching courses, and has been sponsored for research by DePuy Synthes. JRL and GDB declare that they have no competing interests. TDR is an author of several references cited in this topic. CSM has been reimbursed by AO North America and Asia Pacific for being a faculty member during educational conferences.
Peer reviewers
Asif Ilyas, MD
Program Director of Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery
Rothman Institute
Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
Thomas Jefferson University
Philadelphia
PA
Disclosures
AI declares that he has no competing interests.
Isam Atroshi, MD, PhD
Associate Professor of Orthopaedics
Lund University
Chief
Hand Surgery Section
Department of Orthopaedics
Hässleholm and Kristianstad Hospitals
Sweden
Disclosures
Not disclosed.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
წყაროები
ძირითადი სტატიები
Torabi M, Lenchik L, Beaman FD, et al; Expert Panel on Musculoskeletal Imaging. ACR appropriateness criteria: acute hand and wrist trauma. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019 May;16(5s):S7-17.სრული ტექსტი აბსტრაქტი
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Management of distal radius fractures: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Dec 2020 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Mar 2022 [internet publication].სრული ტექსტი
გამოყენებული სტატიები
ამ თემაში მოხსენიებული წყაროების სრული სია ხელმისაწვდომია მომხმარებლებისთვის, რომლებსაც აქვთ წვდომა BMJ Best Practice-ის ყველა ნაწილზე.
დიფერენციული დიაგნოზები
- Wrist strain
- Ligamentous carpal injury
- Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tear
მეტი დიფერენციული დიაგნოზებიგაიდლაინები
- ACR appropriateness criteria: chronic hand and wrist pain
- Prevention of surgical site infections after major extremity trauma: evidence-based clinical practice guideline
მეტი გაიდლაინებიპაციენტის ბროშურები
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Menopause: what is it?
მეტი პაციენტის ბროშურებიშედით სისტემაში ან გამოიწერეთ BMJ Best Practice
ამ მასალის გამოყენება ექვემდებარება ჩვენს განცხადებას