小结
定义
病史和体格检查
关键诊断因素
- cup-to-disk ratio >0.5
- notching of optic nerve cup
- symptomatic peripheral vision loss
- increased intraocular pressure
- scotomas
- loss of nerve fiber layer
- optic disk hemorrhage
其他诊断因素
- corneal hysteresis
危险因素
- intraocular pressure >21 mmHg
- age >50 years
- family history of glaucoma
- genetic abnormalities
- black ethnicity or Hispanic ethnicity
- myopia
- diabetes mellitus
- hypertension
- low ocular perfusion pressure
- thin central corneal thickness
- corneal hysteresis
- calcium-channel blockers
诊断性检查
首要检查
- tonometry
- gonioscopy
- direct ophthalmoscopy
- indirect ophthalmoscopy
- slit-lamp biomicroscopy
- visual field testing
- optical coherence tomography scanning
需考虑的检查
- digital imaging
- pachymetry
- nerve fiber layer analysis
新兴检查
- corneal hysteresis
治疗流程
eye drops preferred or laser trabeculoplasty contraindicated/failed
laser trabeculoplasty preferred or eye drops contraindicated /failed
eye drops contraindicated /failed and rapidly progressive disease
treatment failure
撰稿人
作者
Nishani Amerasinghe, MBBS, BSc(Hons), FRCOphth
Consultant Ophthalmic Surgeon
Glaucoma Specialist
University Hospital Southampton NHS Trust
Southampton
UK
利益声明
NA is president-elect of the UK and Éire Glaucoma Society and has acted as an unpaid advisor to NICE and The Royal College of Ophthalmologists. NA has served on an advisory panel for Santen and has received travel honoraria and speaker's fees from Thea Pharmaceuticals, Santen, and Allergan. NA has received research funding from AbbVie Pharmaceuticals.
Irena Serov-Volach, MD
Senior Glaucoma and Cataract Fellow
Ophthalmology department
Eye Unit
Epsom and St Helier University Hospitals NHS Trust
London
UK
利益声明
ISV has received consultancy/travel fees from Glaukos.
鸣谢
Dr Nishani Amerasinghe and Dr Irena Serov-Volach would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Robert B. Avery and Dr Michael N. Wiggins, the previous contributors to this topic.
利益声明
RBA and MNW declare that they have no competing interests.
同行评议者
Andrew Chen, MD
Assistant Professor
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
利益声明
AC declares that he has received research funding from Janssen LLC.
Sheila Sanders, MD
Professor of Ophthalmology
University of Kentucky
South Limestone
Lexington
KY
利益声明
SS declares that she has no competing interests.
Mohamed Khodeiry, MD
Glaucoma Fellow
University of Kentucky
South Limestone
Lexington
KY
利益声明
MK declares that he has no competing interests.
Roshini Sanders, FRCS, FRCOphth
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Queen Margaret Hospital
Dunfermline
Fife
UK
利益声明
RS declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
参考文献
关键文献
Weinreb RN, Leung CK, Crowston JG, et al. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016 Sep 22;2:16067. 摘要
International Council of Ophthalmology. ICO guidelines for glaucoma eye care. Feb 2016 [internet publication].全文
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Primary open-angle glaucoma preferred practice pattern. Nov 2020 [internet publication].全文
American Academy of Ophthalmology. Primary open-angle glaucoma suspect preferred practice pattern. Nov 2020 [internet publication].全文
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Glaucoma: diagnosis and management. Jan 2022 [internet publication].全文
参考文献
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
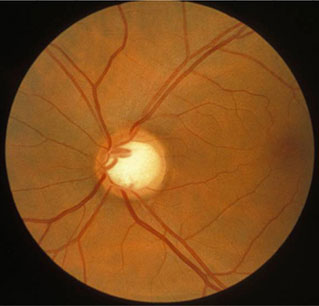
鉴别诊断
- Normal-tension glaucoma
- Angle-closure glaucoma
- High myopia
更多 鉴别诊断指南
- Glaucoma summary benchmarks - 2024
- Trabeculectomy with a biodegradable collagen matrix implant for glaucoma
更多 指南患者教育信息
Glaucoma
更多 患者教育信息登录或订阅即可浏览 BMJ Best Practice 临床实践完整内容
内容使用需遵循免责声明