Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- digoxin exposure
- gastrointestinal symptoms
- central nervous system symptoms
- visual symptoms
Other diagnostic factors
- suicidality
- cardiovascular symptoms
Risk factors
- age >70 years
- decreased renal clearance
- hypokalemia (<3.0 to 3.5 mEq/L)
- concomitant use of specific drugs
- hypomagnesemia
- hypercalcemia
- hypothyroidism
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
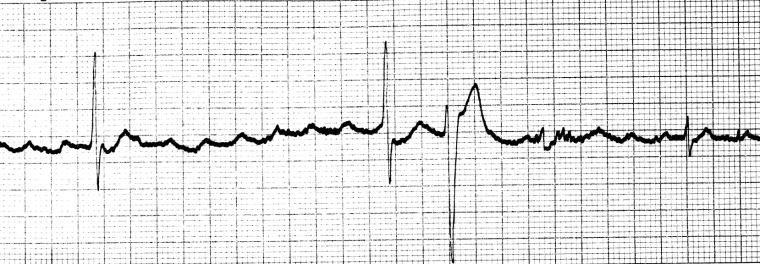
- ECG
- digoxin serum concentration
- serum potassium level
- serum magnesium level
- serum creatinine and BUN
Treatment algorithm
acute ingestion, low to moderate toxicity
chronic ingestion, low to moderate toxicity
severe toxicity or hemodynamic compromise (acute or chronic toxicity)
acute or chronic toxicity after initial treatment
Contributors
Expert advisers
Scott Phillips, MD
Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine
Department of Medicine
University of Colorado
Denver
CO
Clinical Assistant Professor
Department of Pharmacy
University of Washington
Seattle
WA
Chief Executive Officer/Medical Director
Washington Poison Center
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
SP declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Silas Smith for his advice on content in this topic.
Silas Smith MD, FACEP, FACMT
JoAnn G. and Kenneth Wellner Clinical Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine
NYU Langone
Ronald O. Perelman Department of Emergency Medicine
New York
NY
Disclosures
SS's academic medicine organization has received U.S. federal research grants.
Acknowledgements
Dr Scott Phillips would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Oladapo A. Odujube and Dr Robert S. Hoffman, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
OAO and RSH declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Edward W. Boyer, MD
University of Massachusetts Medical School
Worcester
MA
Disclosures
EWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Ruben Thanacoody, MD, FRCP(Edin)
Consultant Physician and Clinical Toxicologist
National Poisons Information Service (Newcastle)
Newcastle-upon-Tyne
UK
Disclosures
RT declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewer acknowledgements
BMJ Best Practice topics are updated on a rolling basis in line with developments in evidence and guidance. The peer reviewers listed here have reviewed the content at least once during the history of the topic.
Disclosures
Peer reviewer affiliations and disclosures pertain to the time of the review.
References
Key articles
Andrews P, Anseeuw K, Kotecha D, et al. Diagnosis and practical management of digoxin toxicity: a narrative review and consensus. Eur J Emerg Med. 2023 Dec 1;30(6):395-401.Full text Abstract
Hack JB, Wingate S, Zolty R, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and management of digoxin toxicity. Am J Med. 2025 Jan;138(1):25-33.e14.Full text Abstract
Reference articles
A full list of sources referenced in this topic is available to users with access to all of BMJ Best Practice.
Differentials
- Beta-blocker toxicity
- Calcium-channel blocker toxicity
- Clonidine toxicity
More DifferentialsGuidelines
- 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline on the evaluation and management of patients with bradycardia and cardiac conduction delay
- Position statement and practice guidelines on the use of multi-dose activated charcoal in the treatment of acute poisoning
More GuidelinesPatient information
Heart attack
Heart failure
More Patient informationLog in or subscribe to access all of BMJ Best Practice
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer